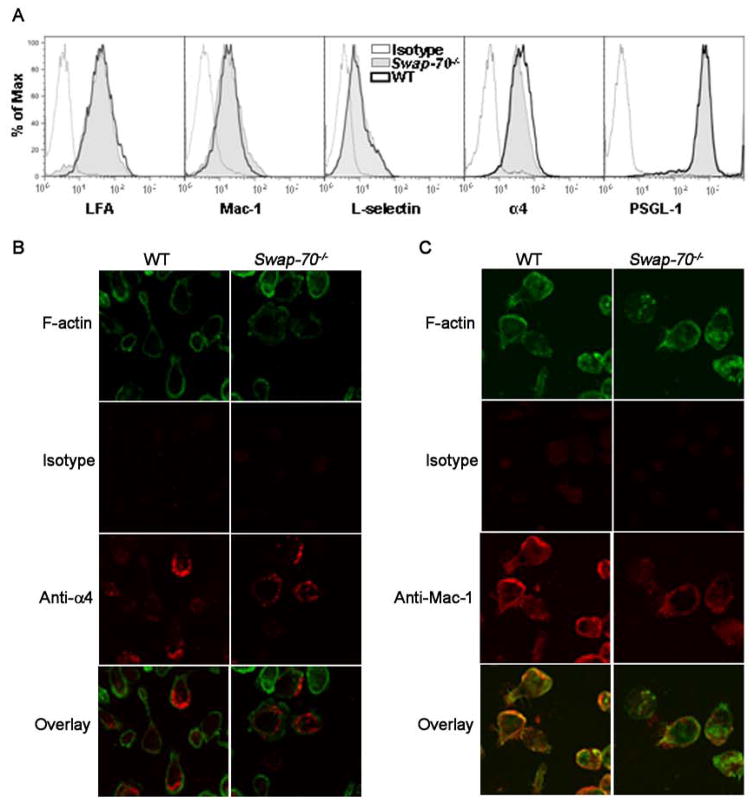
Fig 4. Adhesion molecule distribution is altered in Swap-70−/− eosinophils.
(A) Expression of adhesion molecules by WT and Swap-70−/− eosinophils by flow cytometry. Expression of LFA-1 and α4 was evaluated using rat mAbs against LFA-1 and α4, respectively, followed by FITC-conjugated anti-rat antibodies with rat IgG2b as the isotype control. PE-conjugated rat mAbs against Mac-1 and PSGL-1, and FITC-conjugated rat mAbs against L-selectin were used to evaluate expression of Mac-1, PSGL-1 and L-selectin, respectively. PE- or FITC-conjugated rat IgG2a was used as the isotype control. All antibodies were used at a concentration of 5 μg/ml. (B and C) Immunofluorescence staining to evaluate distribution of α4 and Mac-1 on the cell surface of WT and Swap-70−/− eosinophils adhered to VCAM-1 and ICAM-1, respectively. Adhered cells were first stained with goat anti-mouse α4 (5 μg/ml) or rat anti-mouse Mac-1 (10 μg/ml) followed by rhodamine-conjugated secondary antibodies and then with FITC-phalloidin in buffer containing 0.5% saponin. Goat IgG (for anti-α4) or rat IgG2b (for anti-Mac-1) was used as the isotype control. Magnification × 600. Data shown in A and B is representative of three independent experiments with eosinophils from three different mice for each group.