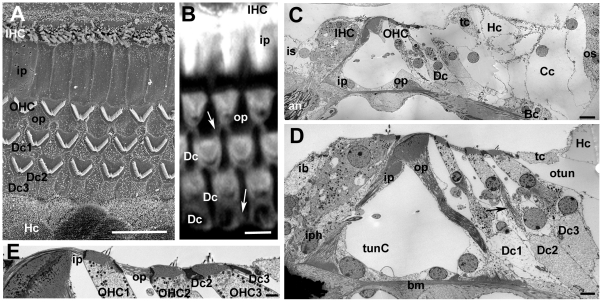
Figure 1. The organ of Corti of the mouse.
Labelling for all figures: OHC = outer hair cell, IHC = inner hair cell; Dc = Deiters' cell, ip = inner pillar cell, op = outer pillar cell, Hc = Hensen's cell, Cc = Claudius cell, Bc = Boettcher's cell, os = outer sulcus, iph = inner phalangeal cell; ib = inner border cell, is = inner sulcus; tunC = tunnel of Corti, otun = outer tunnel; bm = basilar membrane. A. SEM of the apical surface of the organ of Corti (the “reticular lamina”). Each hair cell is separated from its neighbours by intervening supporting cells. The luminal surfaces of the Hensen's cells (HC) are distinguished by numerous microvilli. Scale bar: 10 µm. B. Confocal projection series image at the level of the reticular lamina of phalloidin-FITC labelled whole mount preparation. Phalloidin labels filamentous actin of the hair cell stereocilia, and the cuticular plate beneath the hair bundle in the apical cytoplasm of the hair cell, as well as the filamentous actin associated with the intercellular junctions. The arrow indicates the prominent, thick band of actin associated with the junctions between adjacent supporting cells in the OHC region. Scale bar: 5 µm. C. Montage of low power TEM images of thin section across the organ of Corti of the basal turn to show locations of all the cell types referred to in the text. The central strip of the sensory region containing the hair cells interspersed with specialised columnar supporting cells, is flanked either side with less specialised cells; the cuboidal inner sulcus cells to the inner side, and various cells types to the outer side. Scale bar: 10 µm. D. Thin section of sensory region of the organ of Corti showing some of the structural specialisations of the different supporting cell types. Arrow points to microtubule bundle in Deiters' cell. Bundles of microtubules are especially prominent in the pillar cells. Scale bar: 5 µm. E. The reticular lamina in thin section showing features at intercellular junctions. The head of the inner pillar and outer pillar cell are filled with microtubules, whereas the junction between an outer hair cell (OHC) and a Deiters' cell is characterised by microfilament assemblies, appearing as electron dense structures running the depth of the junction and widely into the supporting cell. Scale bar: 1 µm.