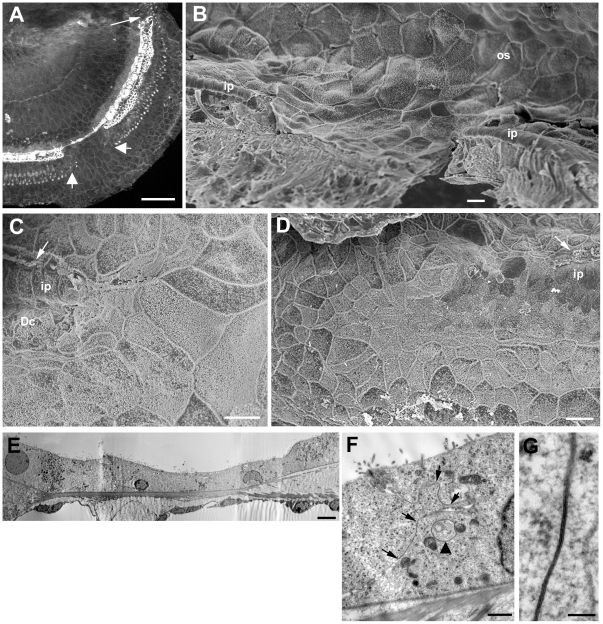
Figure 12. Morphological characteristics of the squamous-like epithelium.
A. C57BL/6 mouse at 6 weeks post-treatment. Actin labelling in whole mount preparation of the apical coil. The arrow indicates the apical tip of the organ of Corti. A patch of the flat epithelium, indicated by the larger arrows, interrupts the strip of repaired epithelium. Scale bar: 100 µm. B. C57BL/6 mouse at 4 weeks post-treatment. Mid-basal region of the cochlea viewed towards the lateral wall (from inside outwards). Pillar cells (ip) are still erect either side of a patch of flattened epithelium. The sheet of flattened epithelial cells is continuous with the cells of the outer sulcus (os). Scale bar: 10 µm. C. Edge of squamous patch where it cuts across the repaired epithelium. The enlarged surfaces of cells that normally reside on the outerside of Deiters' cells curve round the end of the strip containing Deiters' cells (Dc) and pillar cells (ip). IHC still present (arrow). Scale bar: 10 µm. D. The apicalmost tip of the organ of Corti. The surfaces of cells either side of the strip of cells containing Deiters' and pillar cells, curve across the termination point of that strip in a similar pattern to that at the edges of the patches of squamous-like epithelium. The surface features of those cells are also similar to those that create the flat epithelium. Scale bar: 10 µm. E. Thin section through a region of flattened epithelium. The cells across the basilar membrane are all similar in morphology and show relatively few organelles or other cytoplasmic specialisations. Their features are reminiscent of those of Claudius' cells. Scale bar: 2 µm. F and G. Details of cell forming the flat epithelium. The cell cytoplasm is relatively unstructured and there are few organelles. Large gap junction plaques occupy much of the plasma membrane along the contact between adjacent cells. The extent of two gap junctions are defined by the pairs of arrows in panel F, the lower contact region viewed at higher power showing the characteristic thin section morphology of a gap junction. Annular gap junctions are also evident in the cell cytoplasm (arrow in panel F), suggesting continuing turnover of gap junction plaques. Scale bars: 1 µm in F; 0.1 µm in G.