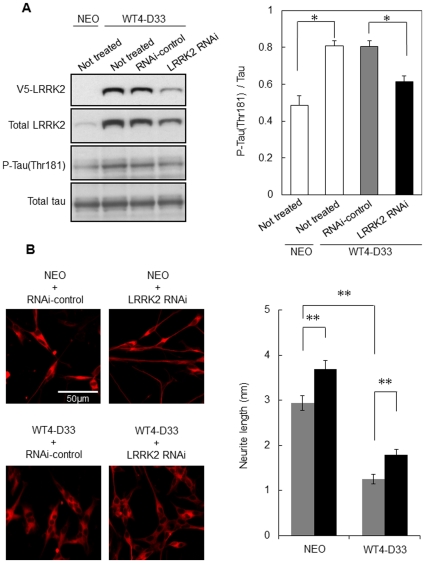
Figure 4. Effect of overexpression and knockdown of LRRK2 on phosphorylation of tau (Thr181) in neuronal cells and their neurite outgrowth.
(A) Left: A SH-SY5Y clone (WT4-D33) expressing V5-tagged wild-type LRRK2 was transfected with either the LRRK2-specific RNAi or the RNAi control. After 48 h of transfection, cell lysates were prepared and subjected to Western analysis using antibodies against V5-tag, LRRK2, phospho-tau (Thr181), and non-phosphorylated tau. A vector control clone (NEO) expressing only the neomycin gene is shown in lane 1. Right: Graphical representation of the tau (Thr181)-phosphorylation level. (B) Left: WT4-D33 and NEO were treated with 10 µM all-trans retinoic acid for 72 h, transfected with the LRRK2-specific RNAi or RNAi-control, cultured for a further 72 h, and subjected to immunostaining with anti-β III tubulin. Right: Graphical representation of neurite length measured using NIH ImageJ software. Stars represent statistical comparisons by one-way ANOVA (n = 3 in A and n = 50 in B); *: p<0.005, **: p<0.001.