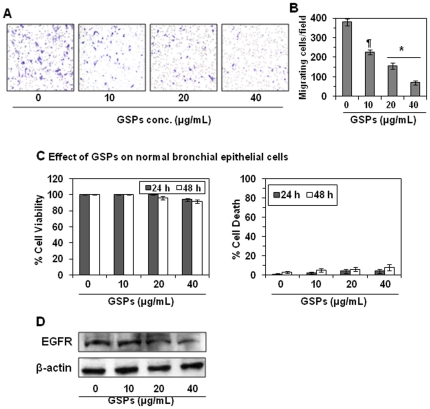
Figure 2. Effect of GSPs on HNSCC cell invasion and EGFR expression.
(A) OSC19 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of GSPs for 48 h and the effects on their invasiveness assessed as described in Figure 1. Crystal violet staining of the membranes showed that, as compared to non-GSPs-treated control cells, the GSPs inhibited invasion of cells in a concentration-dependent manner. (B) The migratory cells were counted and the results expressed as the mean number of invasive cells±SD/microscopic field, magnification: ×10. The values are reported from three separate experiments. Significant inhibition versus non-GSPs-treated control, * P<0.001, ¶ P<0.01. (C) The non-toxic effect of GSPs on normal human bronchial epithelial cells was determined in terms of cell viability and cell death. The data on cell viability are expressed in terms of percent of control cells (non-GSPs-treated) as the mean±SD of 6 replicates. Similarly, the cytotoxic effect of GSPs on normal bronchial epithelial cells was determined using trypan blue dye exclusion assay as described in Materials and Methods and is expressed in terms of percent of dead cells as mean±SD from three experiments. (D) Dose-dependent effect of GSPs on EGFR expression in OSC19 cells. The levels of EGFR in whole cell lysates of OSC19 cells treated with different concentrations of GSPs for 48 h were determined using western blot analysis. Representative blots are shown from three independent experiments.