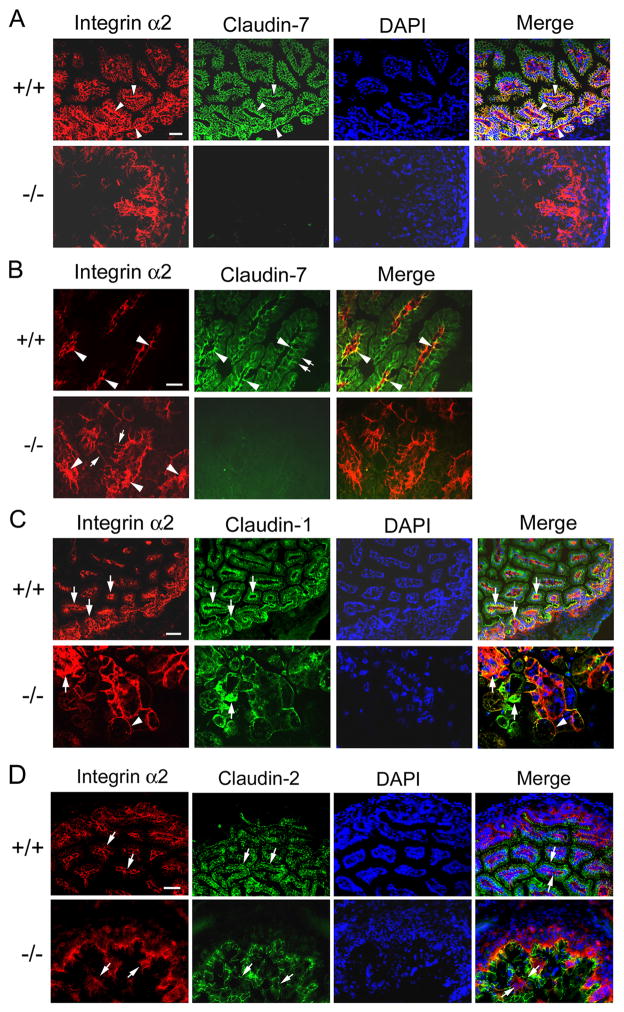
Figure 6.
Disruption of integrin α2 localization in Cldn7−/− intestines. (A) Arrowheads in (+/+) showed examples of double immunostaining signals where claudin-7 and integrin α2 were co-localized at the basal membrane. Integrin α2 signals were disorganized in (−/−). Bar: 40 μm. (B) High magnification to show the co-localization of claudin-7 and integrin α2 in Cldn7+/+ (arrowheads in +/+) and disorganized integrin α2 signal in Cldn7−/− intestines (arrowheads in −/−). The double arrows in (+/+) indicated the apical surface of the villus and arrows in (−/−) pointed to the integrin α2 signal moving towards apical lateral surface. Bar: 20 μm. (C) Integrin α2 and claudin-1 were partially co-localized at the basolateral region of Cldn7+/+ villi (arrows in +/+). Arrows in (−/−) indicated the clustered signals of integrin α2 and claudin-1, while the arrowhead pointed to integrin α2 moving towards the apical lateral surface in the absence of claudin-7. Bar: 40 μm for the top panel and 20 μm for the bottom panel. (D) Claudin-2 and integrin α2 were not co-localized since claudin-2 signal was largely localized at the apical membrane even in the absence of claudin-7 (claudin-2, arrows). Integrin α2 signal (integrin α2, arrows) was mainly in the basolateral region in Cldn7+/+, but was disrupted in Cldn7−/−. Arrows in merge images pointed to claudin-2 (top) and integrin α2 (bottom) signals. Bar: 20 μm.