Fig. 3. Requirements for TrxR1 or glutathione for replication in proliferative hepatocytes in juvenile livers.
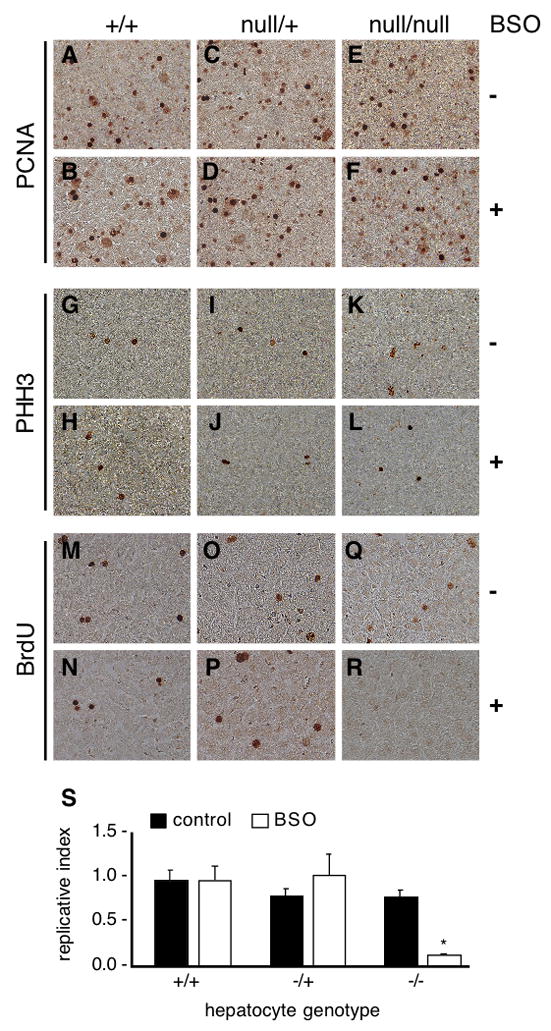
Juvenile (P23–25) wild-type (hepatocytes txnrd1+/+), txnrd1cond/+;albCre1 (hepatocytes txnrd1null/+), and txnrd1cond/null;albCre1 (hepatocytes txnrd1null/null) mice received an I.P. inoculation with saline alone or 50 mg BSO in sterile saline. Four hours later, mice received an I.P. inoculation with 2.5 μmol of BrdU in sterile saline. One hour later, mice were sacrificed and livers were harvested for immunohistological analyses. Global proliferative indexes were assessed by PCNA-staining (Panels A–F) and by analysis of the M phase index by PHH3-staining (Panels G–L). None of the conditions tested affected the percent of proliferative cells in liver (Panels A–L), verifying that the conditions used did not have a major impact on cell survival or general cell physiology within the time-frame of the experiment. Replication was assessed by staining for BrdU (Panels M–R). Images from one animal under each condition are shown to illustrate the methodology that was used and further details are presented in Supplemental Fig. S1. The experiment was repeated on four mice for each condition. For each animal, ~15,000 hepatocyte nuclei (30 fields with ~500 hepatocyte nuclei in each) were assayed. To determine the fraction of proliferative hepatocytes that were able to sustain DNA replication under each condition (“replicative index”), the number of BrdU-labeled hepatocyte nuclei per 15,000 total hepatocyte nuclei was divided by the number of PHH3-labeled nuclei per 15,000 total hepatocyte nuclei for each liver. Quantitative data is presented in Panel S as the mean + S.E.M. for the four animals in each condition. The asterisk indicates the only significantly deviant condition, txnrd1cond/null;albCre1 animals treated with BSO, which was significantly lower than all five other conditions (P < 0.05, Student’s T-test).
