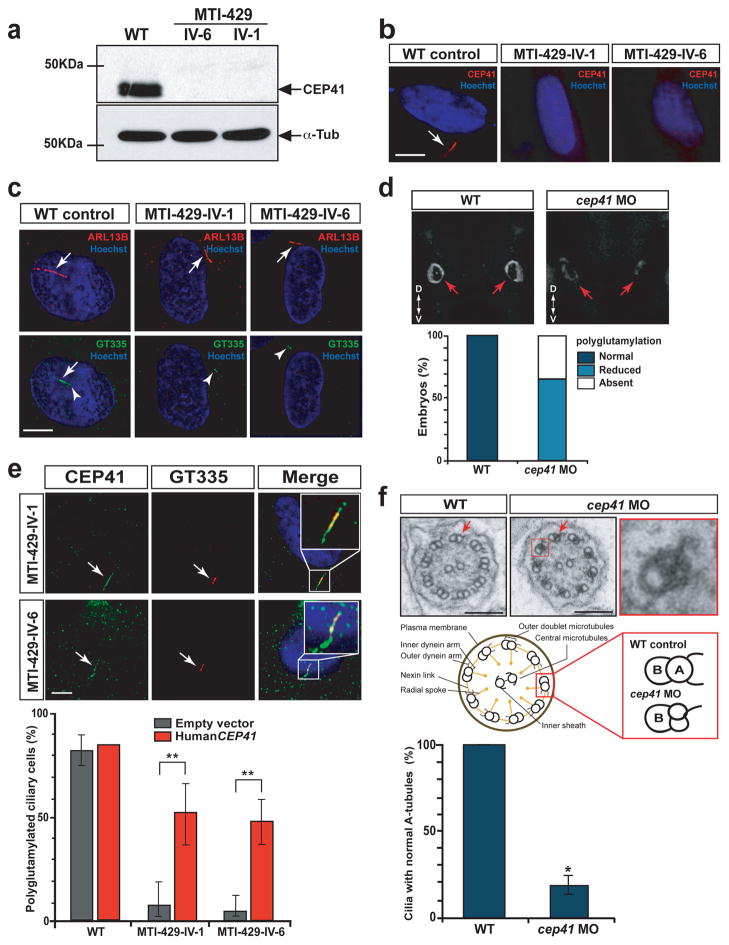
Figure 3.
CEP41 is required for tubulin glutamylation at the ciliary axoneme. (a) Absent CEP41 protein in CEP41 mutant patient cells. (b) Ciliary localization of endogenous CEP41 in human fibroblasts and loss of the protein in CEP41 mutant cilia. Scale bar 5 μm. (c) WT cells have both GT335-positive basal bodies (arrowheads) and cilia (arrows, marked by ARL13B), while mutant cells show staining of GT335 only at the basal bodies. Scale bar 5 μm. (d) Depletion of cep41 causes glutamylation defects in zebrafish olfactory placode cilia (red arrows). Images of GT335-stainined WT and cep41 morphant embryos were taken in anterior view (head is up and tail is down, D, dorsal; V, ventral), quantified below. (e) Exogenous CEP41 expression restores ciliary axoneme glutamylation in CEP41 mutant cells. Arrows: primary cilia stained for CEP41 and GT335. Insets: merged images at higher power, quantified below. Scale bar 5 μm. **P < 0.001; error bars = s.e.m. (f) Ultrastructural analysis of the pronephric ciliary axoneme at 72 hpf zebrafish embryos. Compared to WT, cep41 morphants have A-tubule specific defects in the outer doublet microtubules. Arrows: A-tubules and one of nine outer doublet microtubules is magnified in the red box. The numbers of cilia, categorized in normal and abnormal A-tubules according to the schematic, were counted in both WT embryos and cep41 morphants (n = 3 embryos, >20 cilia per animal), quantified below. Scale bar 100 nm. **P < 0.01; error bars = s.e.m.