Fig. 6.
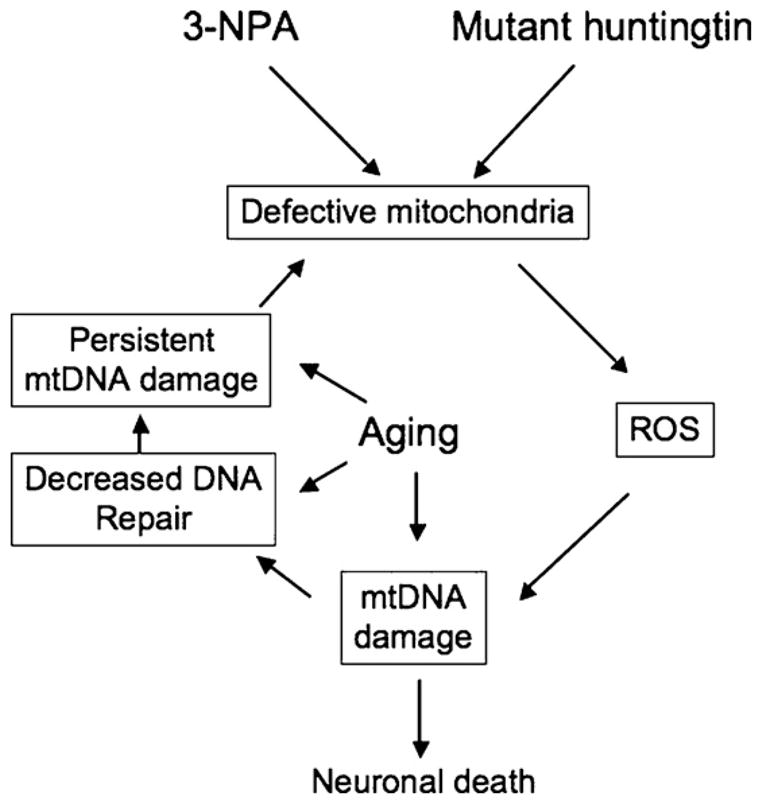
Mitochondrial DNA damage caused by 3-NPA and mutant huntingtin. 3-NPA and mutant hutingtin lead to defective mitochondria, which in turn can lead to increased generation of ROS and extensive mtDNA damage. An age-dependent increase in mtDNA damage and/or a decline in mtDNA repair capacity could lead to persistent mtDNA damage and exacerbate the chemical or huntigntin induced problems, ultimately leading to a marked decline in mitochondrial function, resulting in neuronal death.
