Figure 7.
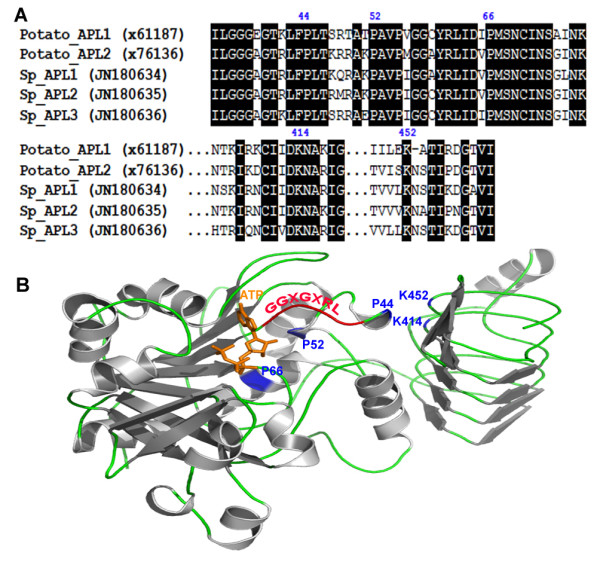
Amino acid sequence alignment for the regulatory sites of APLs between potato and S. polyrhiza and modeled structure of S. polyrhiza APL1. a) GenBank accession numbers were listed in parentheses. Important proline (P44, P52 and P66) and lysine (K414 and K452) residues critical for allosteric regulation were numbered corresponding to potato AGPase large subunit (x61187). Identical residues were shaded in black. b) The N-terminal region containing the putative ATP binding site and the regions containing the putative 3-PGA binding sites of APL1 were modeled by comparison with the known structure of the potato AGPase small subunit (PDB 1yp3) with 54.93% identity. The modeled position of ATP in orange was shown. The α-helix and β-sheet were colored in gray and the loop was in green. Important proline (P) and lysine (K) residues in APL1 were indicated by blue color. The conserved GGXGXRL loop region was in red.
