Figure 1.
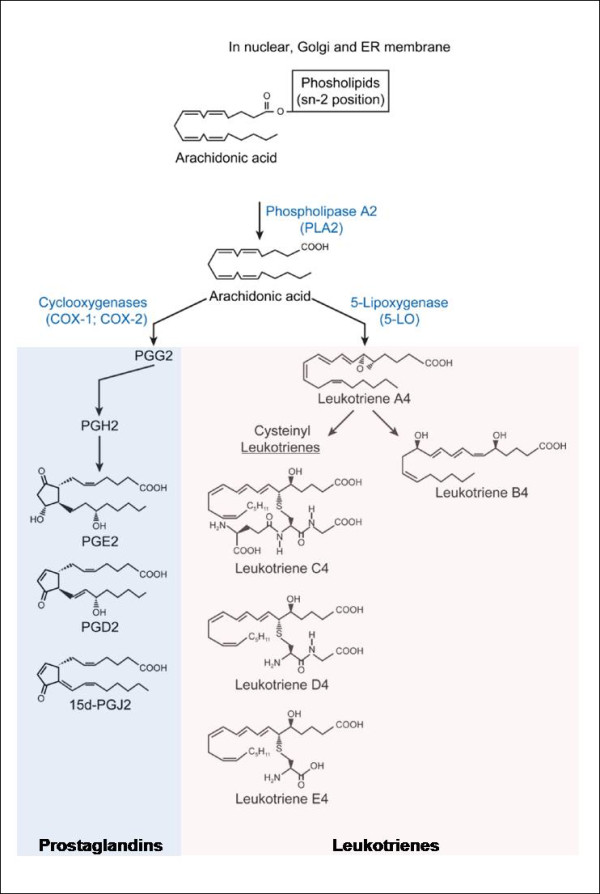
Metabolic pathway of AA transformation into eicosanoid products. Once a cell is activated by a proinflammatory stimulus that engages a Gαq-coupled seven-transmembrane receptor, AA can be cleaved by cytosolic PLA2 from phospholipids that compose cellular membranes (mostly nuclear, endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi membranes)[173]. Free AA can subsequently be converted into different eicosanoid products by different enzymes (represented in blue), notably the COX and LO pathways. This review will mainly focus on the prostanoids - PGE2, and 15d-PGJ2 prostaglandins - and on 5-LO products, namely LTs. Only eicosanoids and pathways of interest in this paper are depicted.
