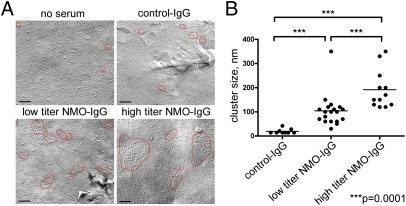
Fig. 3.
(A) Freeze-fracture electron microscopic analysis of mouse astrocytes cultured without and with IgG from control or NMO serum. Unexposed or exposed to control human IgG (∼2 mg/mL), most intramembranous particles are single and distributed uniformly. OAPs (encircled in red) are small and relatively sparse. After exposure for 24 h to IgG prepared from “low-titer” NMO serum (AQP4-binding capacity = 20 nmol/L), OAPs are modestly larger. After exposure to “high-titer” serum IgG (AQP4-binding capacity = 105 nmol/L), OAPs are much larger. (Scale bars, 100 nm.) (B) Scatter plot analysis of OAP size after exposure to control-IgG or NMO-IgG of low or high titer. Horizontal bars correspond to mean values. Differences between values for control-IgG and low-titer NMO-IgG and control-IgG and high-titer NMO-IgG and between low-titer and high-titer NMO-IgG are significant (***P = 0.0001). Differences for OAP cluster sizes in control-IgG and low-titer and high-titer NMO-IgG were compared by the Mann–Whitney test with GraphPad software.