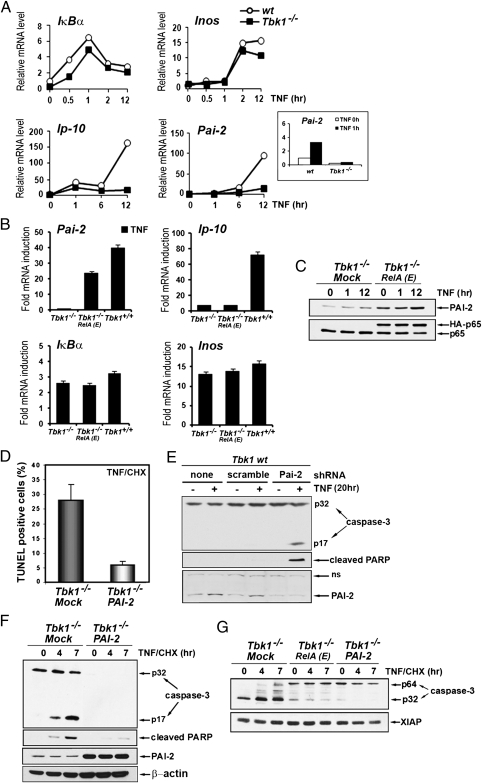
Fig. 3.
TBK-1 controls NF-κB–dependent expression of the survival factor PAI-2. (A) Induction of NF-κB target genes was determined by qRT-PCR amplification of mRNAs prepared from WT and Tbk1−/− MEFs that were stimulated with TNF for the indicated times. Inset: Short time course (0 and 1 h) of Pai-2 mRNA induction in both cell types. (B) Relative mRNA induction was analyzed by qRT-PCR amplification of RNAs prepared from WT (Tbk1+/+), Tbk1−/−, and Tbk1−/− MEFs expressing RelA(S534E), depicted as RelA(E) that were stimulated with TNF for 2 h (IκBα), 6 h (Pai-2 and Inos), or 14 h (Ip10). (C) Expression of endogenous PAI-2 and RelA was examined by immunoblotting in extracts prepared from cells that were stimulated with TNF for the indicated times. (D) Apoptotic cell death, determined by TUNEL assay as described earlier, was quantified in Tbk1−/− MEFs and in cells stably expressing PAI-2 that were stimulated for 3 h with TNF in the presence of CHX. (E) WT MEFs expressing a Pai-2 shRNA or a scrambled shRNA were treated with TNF for 20 h. Caspase-3 activation, PARP cleavage, and protein expression were determined by immunoblotting. (F and G) Caspase-3 activation, PARP cleavage, and protein expression were determined by immunoblotting in extracts prepared from the indicated cells that were stimulated with TNF in the presence of CHX for the indicated times.