Fig. 3.
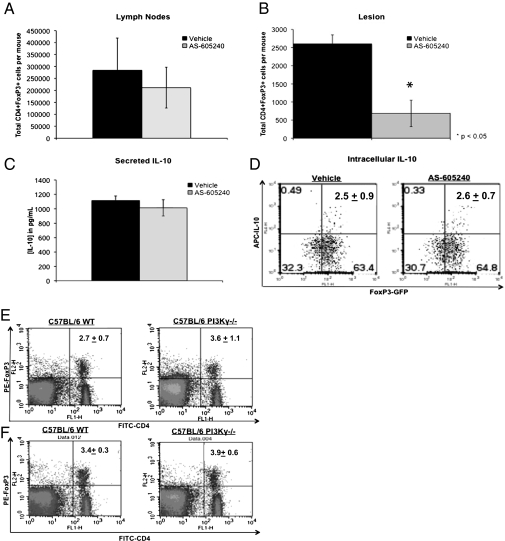
Blockade of PI3Kγ reduces recruitment of CD4+ FoxP3+ Tregs into the lesion but has no effect on Treg function or development. Quantification of CD4+ FoxP3+ Tregs within the lymph nodes (A) and the lesions (B) of vehicle- and AS-605240–treated mice. At 9 wk postinfection, infected mice were killed and CD4+ FoxP3+ cell populations within the lesions and draining lymph nodes were analyzed by flow cytometry. The data shown are the average numbers of CD4+ FoxP3+ Tregs per mouse from each treatment group and represent collective data from three independent experiments with similar results. *P < 0.05 as determined by an unpaired Student's t test. (C and D) Quantification of IL-10 production by GFP+ cells isolated from the spleens of naive FoxP3-EGFP knock-in C57BL/6 mice. Cells were stimulated in vitro with plate-bound anti-CD3/anti-CD28 antibodies in the presence of AS-605240 or vehicle, and IL-10 levels were determined by ELISA (C) and intracellular cytokine (ICC)-flow cytometry (D). ELISA data are expressed as the mean cytokine level (pg/mL) ± SE from three independent experiments with similar results. Data shown for ICC-flow cytometry are from one representative experiment of two with similar results. The effect of PI3Kγ deficiency on Treg populations in C57BL/6 mice is shown. Cells were obtained from the lymph nodes (E) and spleens (F) of naive C57BL/6 WT and PI3Kγ−/− mice and stained using anti-CD4 (FITC) and anti-FoxP3 phycoerythrin (PE) antibodies. C57BL/6 WT and PI3Kγ−/− mice contain comparable proportions of CD4+ FoxP3+ Tregs within their secondary lymphoid organs. Data are presented as the percentage of CD4+ FoxP3+ cell populations ± SE and represent results from one of three independent experiments (n = 3 mice) with similar results.