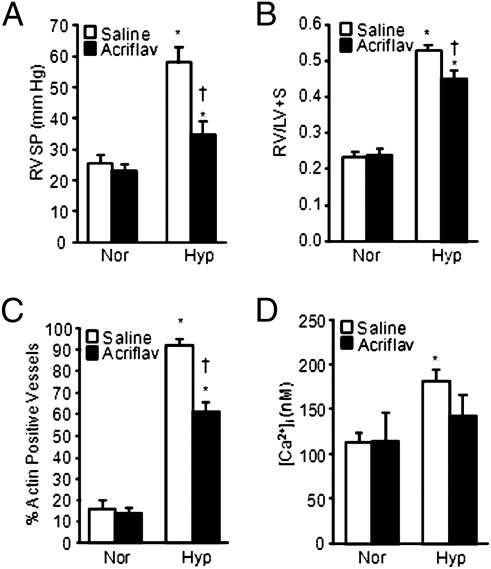
Fig. 5.
Effect of acriflavine treatment on HPH in rats. (A) Effect of acriflavine (acriflav) on RVSP (mean ± SEM) in normoxic (Nor) and chronically hypoxic (Hyp) rats. Rats were injected with saline or 2.0 mg/kg acriflavine per day. (B) RV/LV+S ratio (mean ± SEM) in rats exposed to normoxia or hypoxia in the absence or presence of acriflavine. (C) Percentage of total vessels (mean ± SEM) that were identified as SMA positive in lung sections from normoxic and hypoxic rats treated with saline or acriflavine. In all experiments, n = 5 rats per group. *Significant difference compared to normoxia value within treatment; †significant difference compared to Hyp-saline. (D) Basal [Ca2+]i (mean ± SEM) in PASMCs from normoxic and hypoxic rats treated with saline (n = 94 cells from five rats for normoxia and 92 cells from five rats for hypoxia) or acriflavine (n = 100 cells from five rats for normoxia and 110 cells from five rats for hypoxia).