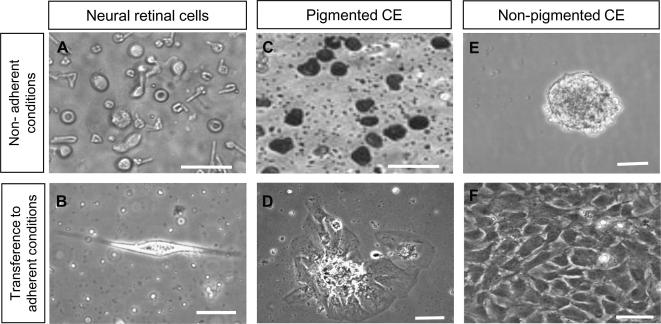
Fig. 2.
Phase-contrast microscopy of cells isolated from the neural retina and CE cultured in suspension for 1 week before transferal to adherent culture conditions (A) Cells isolated from the neural retina did not form spheres when cultured in suspension. (B) Neural retinal cells were able to adhere to tissue culture plates after initial culture in suspension for 1 week. However, these cells did not proliferate. (C) Pigmented CE cells did not adhere after 72 h in suspension culture. (D) When transferred to adherent conditions, pigmented CE cells attach, lost their pigment and acquired a large flattened/epithelioid morphology and did not proliferate. (E) Non-pigmented CE cells formed spheres after 72 h in suspension culture. (F) When cultured under adherent conditions in the presence of EGF, dissociated CE cells from non-pigmented spheres reached confluency by 1 week and displayed a characteristic epithelial morphology. (Scale bars represent 100 μm. CE = Ciliary Epithelium, EGF = Epidermal Growth Factor.)