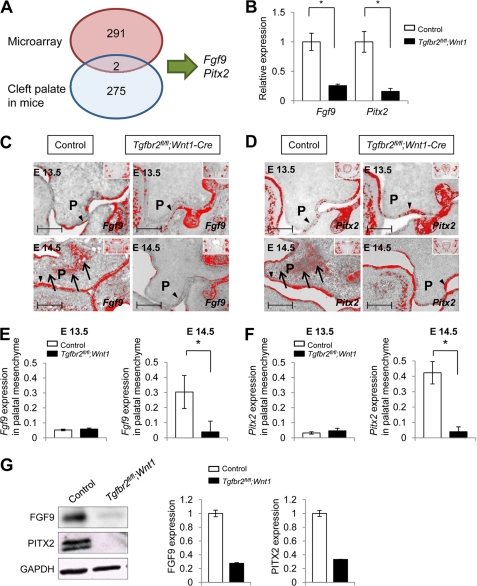
FIGURE 1.
Fgf9 and Pitx2 are down-regulated in Tgfbr2fl/fl;Wnt1-Cre mice at E14.5. A, diagram depicts the strategy used to identify Fgf9 and Pitx2 genes in our approach using the combination of E14.5 palate microarray analysis and known mutations in mice that result in cleft palate phenotypes. B, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Fgf9 and Pitx2 in Tgfbr2fl/fl;Wnt1-Cre (closed columns) mice compared with Tgfbr2fl/fl control mice (open columns) in the palate at E14.5. *, p < 0.05. C and D, in situ hybridization of Fgf9 (C) and Pitx2 (D) in Tgfbr2fl/fl;Wnt1-Cre and Tgfbr2fl/fl mice at E13.5 and E14.5. The arrows indicate expression of Fgf9 and Pitx2 in the palatal mesenchyme of Tgfbr2fl/fl control mice. Arrowheads, Fgf9 and Pitx2 expression in the palatal epithelium of Tgfbr2fl/fl control and Tgfbr2fl/fl;Wnt1-Cre mice. Insets show low magnification of craniofacial regions to indicate global expression pattern of Fgf9 and Pitx2. P, palatal shelf. Bar, 50 μm. E and F, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Fgf9 (E) and Pitx2 (F) in the palatal mesenchyme of E13.5 and E14.5 Tgfbr2fl/fl control (open columns) and Tgfbr2fl/fl;Wnt1-Cre (closed columns) mice. *, p < 0.05. G, immunoblotting analysis of FGF9 and PITX2 in E14.5 Tgfbr2fl/fl control and Tgfbr2fl/fl;Wnt1-Cre palates. The graph shows quantitative densitometry analysis of the immunoblotting data. Error bars, S.D.