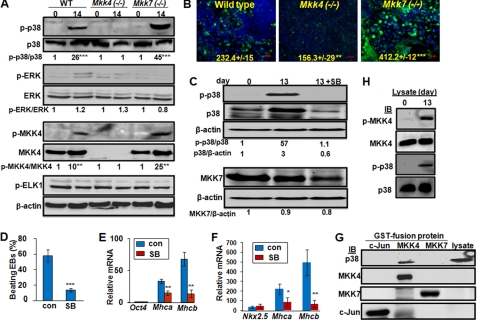
FIGURE 4.
MKK4 is required for p38 activation, while MKK7 attenuates it. Wild type, Mkk4(−/−) and Mkk7(−/−) ESCs were subjected to EB protocol, and (A) cell lysates were obtained at days 0 and 14 of differentiation, and were subjected to Western blotting using antibodies as indicated. The relative levels of phospho- versus total-proteins were calculated based on the immunoblotting intensity of four experiments, and were compared with the level in undifferentiated wild type ESCs, set as 1. Statistical analyses were done by comparing the values in differentiated to that in un-differentiated cells of each genotype. B, EBs at 14 days of differentiation were subjected to immunostaining for p-p38 while nuclei were stained by Hoechst (blue). Pictures were taken under fluorescence microscopy. The relative fluorescence density was quantified by comparing intensity of FITC to that of Hoechst, and results are means ± S.D. of at least three slides. Statistic analyses were done by comparing to the relative fluorescence in wild type cells. Scale bars represent 50 μm. The wild type EBs were either un-treated or treated with the p38 inhibitor, SB202190 (5 μm), at days 6–13 of differentiation, and (C) cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies as indicated, and the relative band intensity was labeled based on calculations using that in undifferentiated wild type ESCs set as 1, (D) number of EBs developed rhythmic beating was counted under light microscopy and the percentage of beating versus total EBs was calculated, and (E) expression of Oct4, Mhca and Mhcb was determined by real-time RT-PCR. F, pNkx2.5PuroIRES2eGFP ESCs were either un-treated or treated with the p38 inhibitor at days 6–13 of differentiation, and expression of Nkx2.5, Mhca, and Mhcb was determined by real-time RT-PCR at 13 day of differentiation. The relative expression values were normalized to Gapdh and results shown are mean ± S.D. from at least three experiments. Statistic analyses were done by comparing to that in cells without p38 inhibitor treatment. All results are means ± S.D. of at least three experiments. Statistical analyzes were done by comparing the values in SB treated samples to the control. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; and ***, p < 0.001 were considered significant. G, lysates (500 μg) from Mkk4(−/−)Mkk7(−/−) ESCs were mixed with bacterially expressed and purified GST-c-Jun, GST-MKK4, and GST-MKK7, as labeled, followed by the GST-beads pull-down assays. The pull-down proteins were examined by Western blotting using antibodies as indicated and cell lysates (50 μg) were loaded directly to the gel as a positive control. H, lysates (100 μg) of either undifferentiated or differentiated wild type ESCs were mixed with GST-MKK4 for an in vitro kinase assay. The GST-MKK4 was then purified by GST-beads and was either directly examined by Western blotting using anti-p-MKK4 and anti-MKK4 (top 2 panels), or applied to an in vitro kinase assay using GST-P38 as a substrate. The kinase reaction was loaded onto SDS-PAGE and examined using anti-p-p38 and total p38, as indicated (bottom 2 panels).