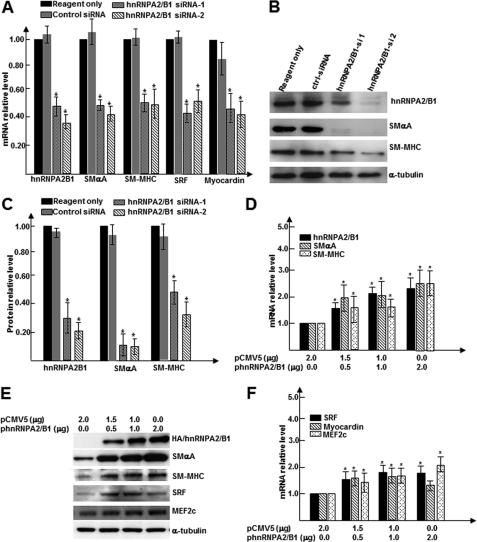
FIGURE 2.
hnRNPA2/B1 is critical for SMC differentiation from ES cells. A–C, hnRNPA2/B1 knockdown down-regulated SMC-specific transcription factors and SMC markers. Two sets of hnRNPA2/B1-specific small interfering RNAs (hnRNPA2B1si-1 and -2) and random siRNA controls were transfected into day 3 differentiating ES cells; after an additional 2–3 days of culture, total RNA and protein were harvested and subjected to RT-qPCR (A) and Western blot analyses (B and C). B shows the representative images, and C shows bar graphs representing means ± S.E. of densitometric analysis (n = 3) of the relative protein levels of target proteins. D–F, hnRNPA2/B1 overexpression enhanced collagen IV-induced SMC differentiation. Undifferentiated ES cells were nucleofected by nucleofector II with different amounts of hnRNPA2/B1 expression plasmids pCMV5-Hnrnpa2/b1. Nucleofected cells were plated on dishes coated with 5 μg/ml of collagen IV and cultured for 3–4 days in DM. Total RNA and protein were harvested and subjected to RT-qPCR analysis for SMC gene expression (D), transcription factors (F), and Western blot analysis (E). An appropriate amount of empty vector pCMV5 was included as plasmid amount compensation. Same amount of protein was loaded into each well, blotted, and probed with specific antibodies for HA (represents exogenous hnRNPA2/B1), SMαA, SRF, MEF2c, and SM-MHC. α-Tubulin was included as internal control (B and E). The data presented here were representative or an average of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05 versus control.