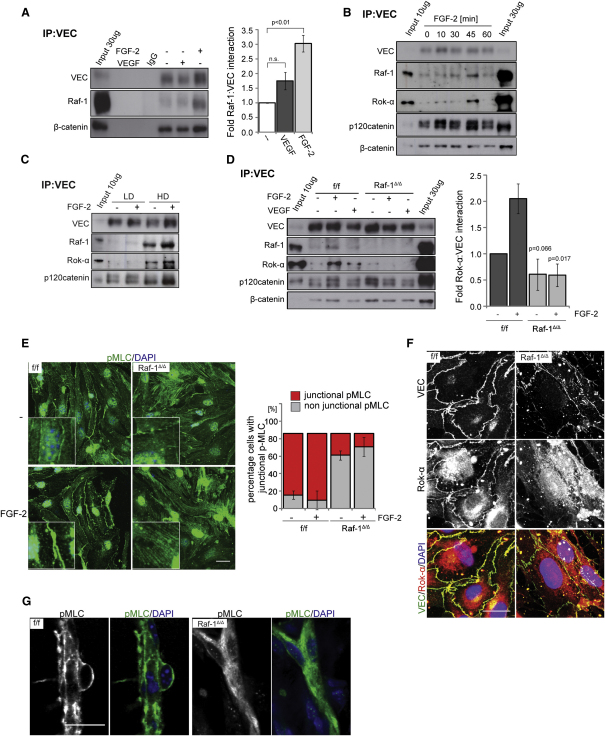
Figure 3.
Raf-1 Is Required for the Recruitment of Rok-α to AJ and for Junctional Myosin Activation
(A–C) Growth factors and increasing cell densities induce the recruitment of Raf-1 and Rok-α to VEC. iMECs were treated with FGF-2 or VEGF (both 50 ng/ml) for 30 min (A) or with FGF-2 (50 ng/ml) for the indicated times (B) or seeded at low (LD) or high density (HD) (C). VEC immunoprecipitates were prepared and the presence of VEC and coimmunoprecipitating proteins was detected by immunoblotting. In (A), the right panel shows growth factor-induced recruitment of Raf-1 to VEC plotted as fold Raf-1-VEC interaction in unstimulated cells (set as 1; mean ± SE of four experiments).
(D) Raf-1 is required for growth factor-stimulated recruitment of Rok-α to VEC. iMECs were treated with FGF-2 or VEGF as in (A). The right panel shows FGF-2 induced recruitment of Rok-α to VEC plotted as fold Rok-α–VEC interaction in unstimulated cells (set as 1; mean ± SE of three experiments). The p value was calculated by comparing f/f versus Raf-1Δ/Δ cells.
(E) pMLC is not associated with AJ in Raf-1Δ/Δ iMECs. iMECs were stimulated with FGF-2 (50 ng/ml) for 30 min. pMLC (green) and DAPI (blue) were visualized by confocal microscopy. The percentage of cells positive for junctional pMLC (mean ± SD) is shown in the lower panel.
(F) Rok-α does not colocalize with VEC in Raf-1Δ/Δ iMECs. Rok-α (red) and VEC (green) were visualized by confocal microscopy. DAPI was used as a counterstain. Scale bar: 20 μm.
(G) pMLC fails to localize at cell-cell borders in sprouts formed in matrigel plugs implanted in Raf-1Δ/ΔEC mice. Scale bar: 20 μm. In (A), IgG represents control immunoprecipitate using an unrelated, isotype-matched antibody, instead of the VEC antibody. In (A)–(D), input = whole cell lysate. See also Figure S3.