Figure 3.
ABC transporters involved in cellular detoxification.
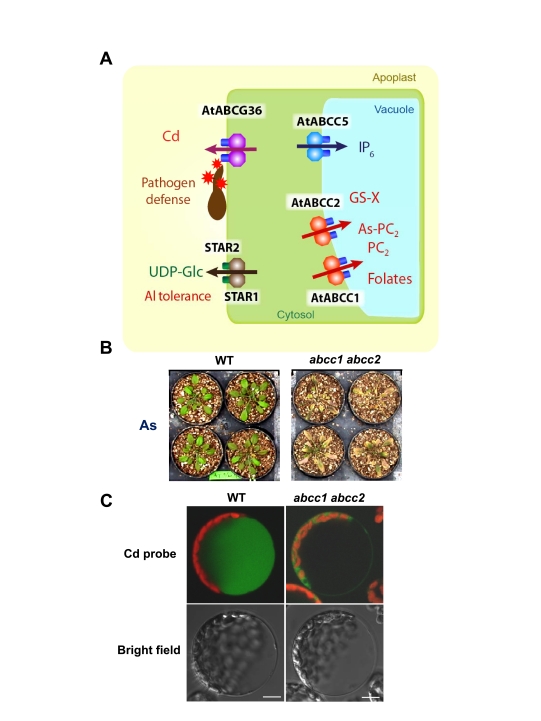
(A) At the plasma membrane, AtABCG36 mediates Cd export and is also involved in pathogen defense (Kobae et al., 2006; Stein et al., 2006; Kim et al., 2007; Bednarek et al., 2009; Clay et al., 2009). The bacterial-type ABC transporters, STAR1 and STAR2, confer aluminum tolerance by transporting UDP-glucose to the extracellular space (Huang et al., 2009; Huang et al., 2010). At the vacuolar membrane, AtABCC1 and AtABCC2 sequester arsenic-phytochelatin complexes in the vacuolar lumen and confer tolerance to toxic metals/metalloid (Song et al., 2010; Park et al., 2011). AtABCC1 is also implicated in folate transport (Raichaudhuri et al., 2009), while AtABCC2 is the major transporter of glutathione conjugate (Lu et al., 1998; Frelet-Barrand et al., 2008). AtABCC5 functions as a phytate transporter (Nagy et al., 2009).
(B–C) Loss-of-function of AtABCC1 and AtABCC2 resulted in arsenic hypersensitivity (Song et al., 2010) (B) and inhibition of vacuolar sequestration of Cd (Park et al., 2011) (C).