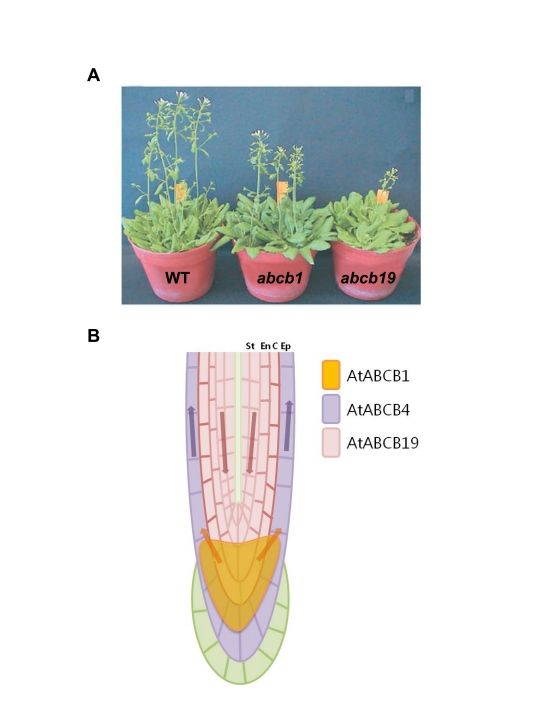
Figure 4.
AtABCB1, AtABCB4, and AtABCB19 are auxin transporters.
(A) Phenotypes of the loss-of-function mutants of AtABCB1 and AtABCB19. Image reprinted Geisler et al. (2005) with permission from Wiley-Blackwell Publishing.
(B) Localization of AtABCB1, AtABCB4, and AtABCB19 in roots and auxin fluxes mediated by these three ABCB proteins. AtABCB1 is expressed in the root differentiation zone (orange, columella and root apical meristem; Sidler et al., 1998). AtABCB4 localizes mainly to the epidermis (purple; Terasaka et al., 2005; Wu et al., 2007). AtABCB19 is expressed from the stele to the cortex and weakly in epidermal cells of the root (pink; Wu et al., 2007; Blakeslee et al., 2007). St: stele, En: endodermis, C: cortex, and Ep: epidermis. The arrows represent auxin flux.