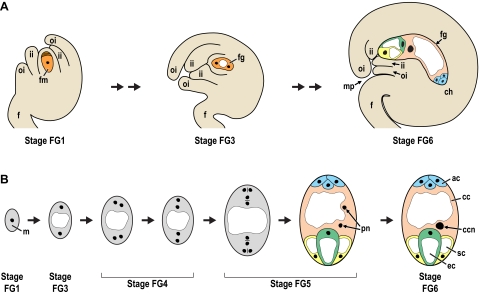
Figure 3.
Megagametogenesis in Arabidopsis.
(A) Steps of megagametogenesis emphasizing development within the ovule.
(B) Stages of megagametogenesis (Christensen et al., 1998). The megaspore contains a single nucleus (stage FG1). This nucleus undergoes two rounds of mitosis, producing a four-nucleate coenocyte, with two nuclei at each pole separated by a large central vacuole (stage FG4). During a third mitosis, phragmoplasts and cell plates form between sister and non-sister nuclei and the nuclei become completely surrounded by cell walls (Stage FG5). During cellularization, the polar nuclei migrate toward the center of the female gametophyte and fuse before fertilization. These events produce a seven-celled structure consisting of three antipodal cells, one central cell, two synergid cells, and one egg cell. If the female gametophyte is not fertilized, the antipodal cells eventually degenerate (Stage FG7, not shown).
White areas represent vacuoles and black circles/ovals represent nuclei.
Abbreviations: ac, antipodal cells; cc, central cell; ccn; central cell nucleus; ch, chalazal region of the ovule; ec, egg cell; f, funiculus; fg, female gametophyte; fm, functional megaspore; ii, inner integument; m, megaspore; mp, micropyle; oi, outer integument; pn, polar nuclei; sc, synergid cells.