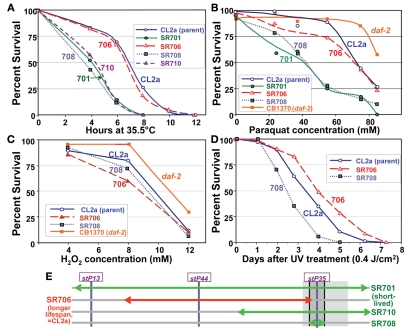
Figure 7.
Stress-survival assays. Worms of each line were grown as synchronous cultures at 20°C. Hermaphrodites were picked as L4 larvae and tested as young adults 1–4 days later. Nematodes were scored as dead if they failed to move spontaneously or in response to prodding. SR701 is an lsq4-congenic line, retaining the Bergerac-BO-derived lsq4 region of chromosome IV in a CL2a background; CL2a is the parental wild-type strain; and SR706, 708 and 710 are recombinant-congenic lines derived from SR701 during the last two generations of backcrossing into CL2a (see Figure 4). CB1370 is a daf-2 mutant strain bearing the e1370 hypomorphic allele (life-span ∼2× wild-type) in a Bristol-N2 background. (A) Thermotolerance assays. Worms were picked as L4 larvae in groups of ≥50, onto agar/NGM plates, and tested as pregravid young adults 1 day later. Survival was assessed at 2-h intervals during incubation at 35.5 ± 0.4°C. (B) Paraquat resistance assays. Adult worms at 3 days post-hatch were transferred in groups of 30 to liquid survival medium without E. coli. After 30 min for digestion of enteral bacteria, paraquat was added to a final concentration of 0–85 mM and replaced daily, with assessment after 3 days at 20°C. (C) Hydrogen peroxide resistance assays. Congenic and recombinant-congenic lines, and parental strain CL2a, were exposed to varying concentrations of hydrogen peroxide (0, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 mM). Mature adult hermaphrodites were treated and the number of live worms was counted after 4 h of continuous exposure. (D) Survival of ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. Groups of 30 worms, 4 days post-hatch, were placed on agar plates without food at 20°C, and exposed to ultraviolet light at 0.4 joules/cm2. Worms were transferred to fresh plates seeded with E. coli (var. OP50); viability was assessed as above at 20.0 ± 0.4°C, at 1-day intervals. (E) Schematic of QTL-mapping data for resistance to temperature shift, paraquat or UV.