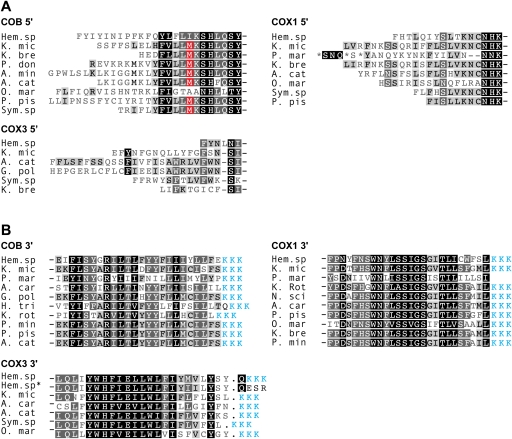
FIG. 2.—
Absence of conventional start and stop codons represented in protein alignments of dinoflagellate COB, COX3, and COX1. Predicted amino acid sequence termini represent (A) 5′ and (B) 3′ sequences from cDNAs. Sequence marked with “*” represents gDNA. Blue sequence represents the conceptual translation of 3′ oligo-A tails of mRNAs. Identical and similar residues are represented by black and gray background, respectively. Methionine residues highlighted in red correspond to potential start codons in cob cDNAs (see text). Dinoflagellate taxa and accession numbers: K. mic, Karlodinium micrum, this study; Hem. sp, Hematodinium sp., this study; K. bre, Karenia brevis, CO065693, EX967108, CO517356, CO059546; P. don, Prorocentrum donghaiense, FJ418633; A. min, Alexandrium minutum, GW798579; A. cat, Alexandrium catenella, AB374233, AB374235, AB374233; O. mar, Oxyrrhis marina, EF680823, EF680822; P. pis, Pfiesteria piscicida, AF463413, AF357518; Sym. sp., Symbiodinium sp., EH037582, EH037973, FE864081; G. pol, Gonyaulax polyedra, AF142470; A. car, Amphidinium carterae, CF064846, CF065669, CF064811; L. pol, Lingulodinium polyedrum, CD810189; K. rot, Katodinium rotundatum, EF036556, EF036582; H. tri, Heterocapsa triquetra, EF036554; P. min, Prorocentrum minimum, AY030285, AF463415; N. sci, Noctiluca scintillans, EF036583.