Figure 6. Phosphorylation of serine residue 463 controls the inhibitory effect of CRN2 on actin polymerization.
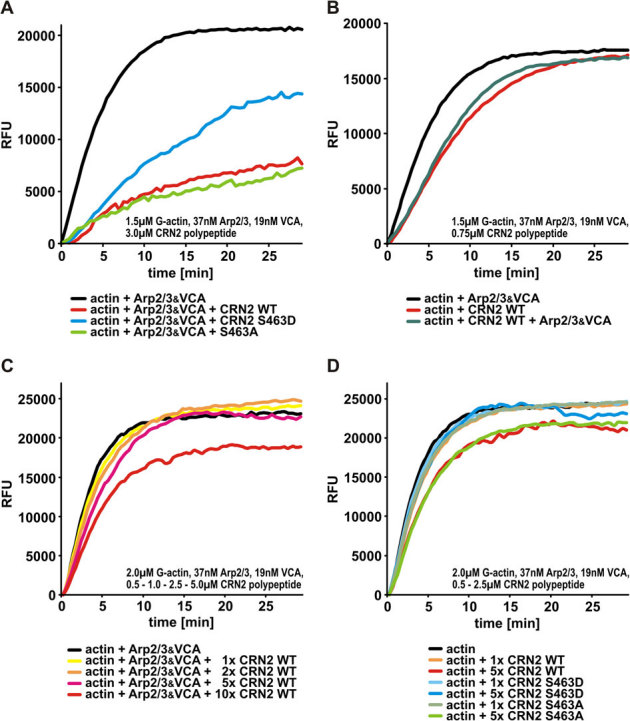
(A) CRN2 wild-type and S643A mutant but not phosphomimetic S463D C-terminal polypeptides effectively inhibit actin polymerization in the presence of Arp2/3 complex. CRN2 reduces the actin polymerization velocity as well as the final amount of F-actin. In this assay a molar ratio of CRN2:actin of 2∶1 was used in order to enhance the effects and visualize differences between the CRN2 polypeptides. For details of the experimental setup see Materials and Methods section. RFU, relative fluorescent units. (B) CRN2 C-terminal polypeptides and the Arp2/3 complex exhibit opposite effects on actin polymerization. The addition of Arp2/3 complex (together with VCA) partially antagonizes the inhibitory effect of CRN2 and increases the actin polymerization velocity. In this assay a molar ratio of CRN2:actin of 1∶2 was used. (C) CRN2 shows a dose-dependent inhibitory effect on actin polymerization. Increasing concentrations of wild-type CRN2 C-terminal polypeptide only decrease the actin polymerization velocity at first (best visible at the time point of 5 min). At the highest CRN2 concentration used the final amount of F-actin also is reduced. In this assay the molar ratio of CRN2:actin was 1∶4 to 2.5∶1. (D) CRN2 wild-type and S463A mutant but not phosphomimetic S463D C-terminal polypeptides affect actin polymerization (in absence of Arp2/3) in a dose-dependent manner. S463D mutant CRN2 neither reduces the actin polymerization velocity nor the final amount of F-actin. In this assay the molar ratio of CRN2:actin was 1∶4 to 1.25∶1.
