Figure 7.
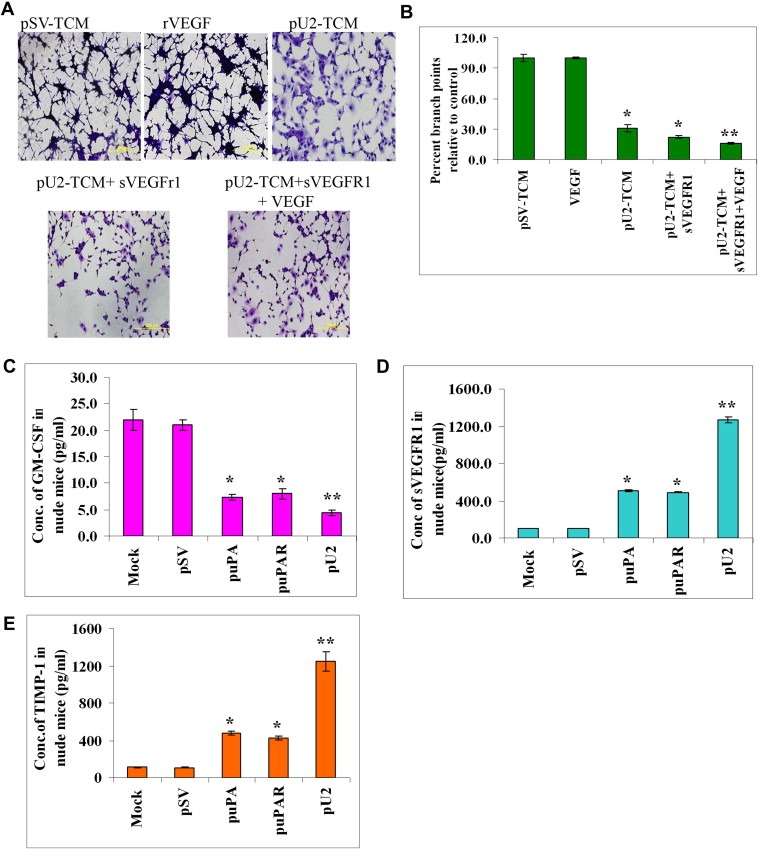
Exogenous addition of SVEGFR1 enhances inhibition of capillary tube formation as shown by in vitro angiogenesis assay. (A) HMECs treated with conditioned media from U87MG cells, which were left untreated or treated with pU2 and/or supplemented with sVEGFR1 and VEGF alone were cultured with the collected conditioned medium in 48‐well plates for 24h. After the incubation period, the medium was removed, and the cells stained with Hema‐3 stain and examined under a microscope. (B) Quantification of angiogenesis in endothelial cells that were left untreated, treated with pU2 conditioned medium, or treated with pU2 conditioned medium supplemented with SVEGFR1. Values are mean±S.D. from three different experiments. (C–E) shRNA against uPA/uPAR inhibits secretion of GM‐CSF and enhances SVEGFR1 and TIMP‐1 secretion in pre‐established intracranial tumors in nude mice. U87MG cells in suspension (2×106 in 10μL serum‐free medium) were injected intracranially in nude mice. One week later, the mice were injected with either pSV or shRNA‐expressing vectors (puPA, puPAR and pU2) using an Alzet mini‐osmotic pump (constructs diluted to 1.5μg/mL in PBS and injected at 0.25μg/h, with 5 mice in each group). After a five‐week follow‐up period, mice were sacrificed, and blood was collected and serum was separated to assay for the levels of mSVEGFR1 (C) and msGM‐CSF (D) and mTIMP‐1 (E) by ELISA according to the manufacturer's instructions.
