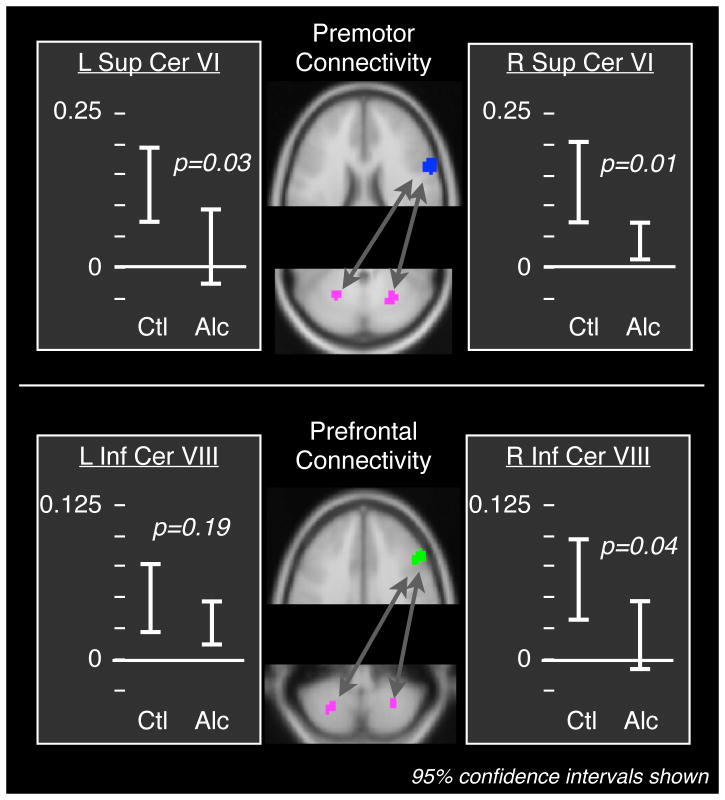
Figure 2. Fronto-cerebellar functional connectivity was lower in alcoholic patients than in matched healthy controls.
The seed regions are indicated in blue (premotor) and green (prefrontal); the cerebellar target regions are magenta. The alcoholic patients exhibited a significant reduction in connectivity between premotor cortex and Lobule VI in superior cerebellum, and between prefrontal cortex and Lobule VIII in inferior cerebellum (see Table 3). Connectivity between a number of other regions did not differ between patients and controls (Table 4), suggesting that the result was specific to fronto-cerebellar circuits.