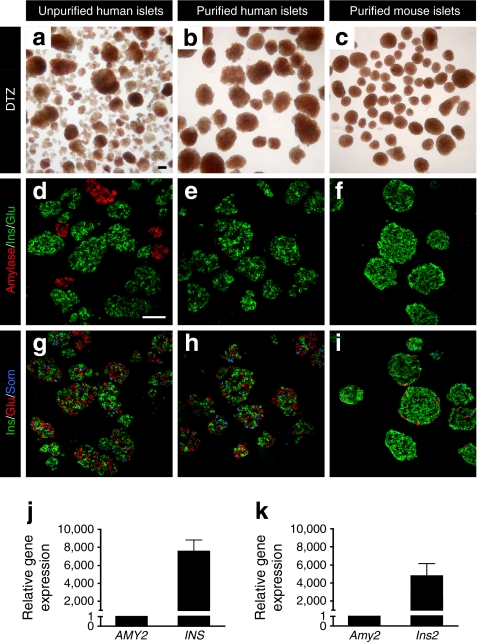
Fig. 1.
Human islets were isolated by handpicking under microscopic guidance. a An example of a human islet preparation received from an islet isolation facility and stained by dithizone (DTZ) before and (b) after the handpicking procedure. While this example was one of the more impure preparations studied (stated purity 50%), all islet preparations contained ductal and acinar fragments. During culture, acinar fragments rounded up and became similar in size and shape to human islets. These acinar structures could only be distinguished from islets by the lighter brown colour of human islets noted by experienced observers. In contrast, isolated mouse islets were much easier to distinguish from acinar tissue fragments and could readily be identified for handpicking. c An example of mouse islets stained by DTZ after handpicking. Scale bar (a–c) 100 μm. To further evaluate the purity of handpicked islets (d–f), selected islet preparations were processed for cryosections and labelled for insulin (Ins, green), glucagon (Glu, green) and α-amylase (red). The islet cell composition of human and mouse islets was similar to that observed in a previous report [3]. Note (d) that the size of some acinar fragments (amylase-positive) is similar to that of islets. Adjacent sections (g–i) were labelled for insulin (green), glucagon (red) and somatostatin (Som, blue). Note the difference in islet cell distribution between human and mouse islets. Scale bar (d–i) 100 μm. j High enrichment of human (n = 6) and (k) FVB mouse islet preparations (n = 4) for beta cells vs acinar cells was demonstrated by quantitative RT-PCR