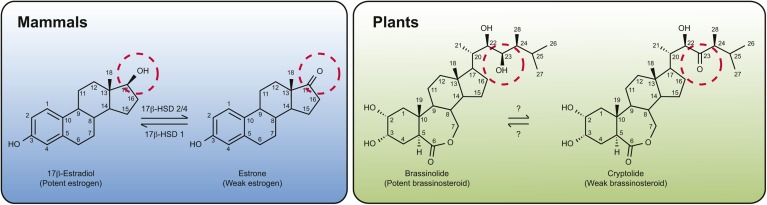
Fig. 3.
Structure and interconversion of steroid hormones in animals and plants. In mammals, 17β-estradiol, a potent estrogen-type hormone that contains a hydroxyl group at the 17th position (circled), is dehydrogenated by 17 β-HSD 2/4 to produce a less active ketone-containing estrone, whereas 17 β-HSD 1 can catalyze the reverse reaction. In an analogous manner, in plants, the 23-hydroxyl group of BL (circled) can be dehydrogenated to produce a ketone-containing derivative called cryptolide. The enzyme(s) responsible for this interconversion, however, is not known.