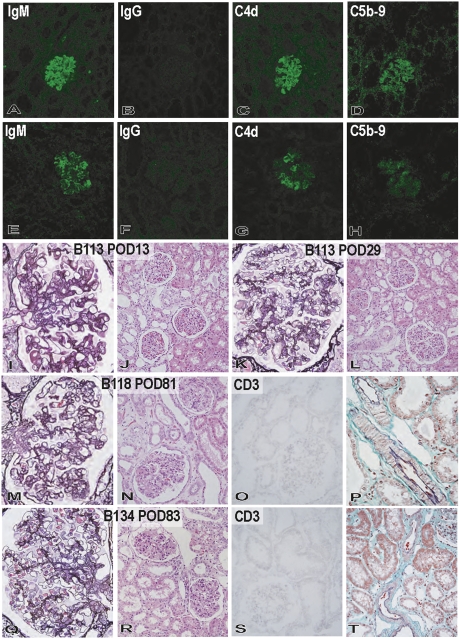
Figure 5.
Pathologic changes in the grafts of the immunotolerance protocol. In reversible glomerular injury in B113, deposition of IgM (A), C4d (C), and C5b-9 (D), but not IgG (B), occurred by postoperative day 13 (A–D: original magnification, ×200), and mild thrombotic microangiopathic glomerulopathy developed (I: periodic acid-methenamine [PAM] stain; original magnification, ×600). Cellular rejection and arteriolar changes were not detected at postoperative day 13 in B113 (J: hematoxylin and eosin stain; original magnification, ×200). However, these glomerular alterations recovered to almost their structure by postoperative day 29 in B113 (K: PAM stain; original magnification, ×600). Cellular rejection, arteriolar changes, and interstitial fibrosis did not develop at postoperative day 29 in B113 (L: hematoxylin and eosin stain; original magnification, ×200). In the graft with unstable graft function (B118), focal mesangial proliferation with double contour of glomerular basement membrane were seen at postoperative day 81 (M: PAM stain; original magnification, ×600). Focal interstitial fibrosis was noted, but cellular rejection and arterial changes were not detected (N: hematoxylin and eosin stain; original magnification, ×200; O: CD3 stain; original magnification, ×200; P: elastica-Masson Goldner stain; original magnification, ×600). In the graft with stable graft function (B134) at postoperative day 83, focal and weak deposition of IgM (E), C4d (G), and C5b-9 (H) was seen, but no deposition of IgG (F) was noted (E–H: original magnification, ×200). The glomeruli showed no obvious glomerulopathy at postoperative day 83 in B134 (Q: PAM stain; original magnification, ×600) with no cellular rejection or vascular changes (R: hematoxylin and eosin stain; original magnification, ×200; S: CD3 stain; original magnification, ×200; T: elastica-Masson Goldner stain; original magnification, ×200). POD, postoperative day.