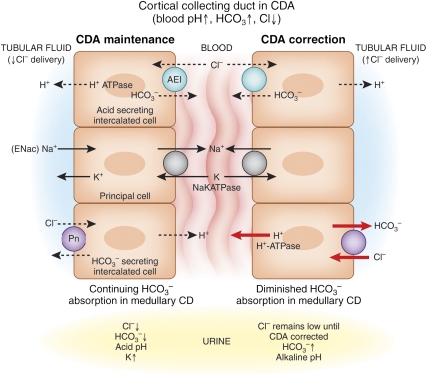
Figure 1.
In the CCD during reduced Cl− delivery to that segment in CDA, pendrin activity is increased but secretion of HCO3− is inhibited by insufficient Cl- for anion exchange. HCO3− reabsorption may be partly maintained by Na+/H+ exchange by the electrical coupling between the principal cell and the H+-secreting A cell (although it is morphologically less active than normal17) and by the remainder of the collecting duct in the medulla. Coupled Na+/K+ exchange causes kaliuresis. After Cl− delivery to the cortical collecting ducts increases, HCO3− secretion occurs and medullary HCO3− reabsorption diminishes,32 allowing correction of the hypochloremic alkalosis. In our rat studies, bicarbonaturia occurred within minutes of Cl− administration intravenously and Cl− did not increase in the urine until correction of serum [Cl−] was nearly complete. (Both H+ and HCO3− are produced in the A- and B-type cells by carbonic anhydrase, and during acute acid-base changes, pendrin and H+ ATPase shuttle back and forth from cytosol to the luminal or basolateral membrane18).