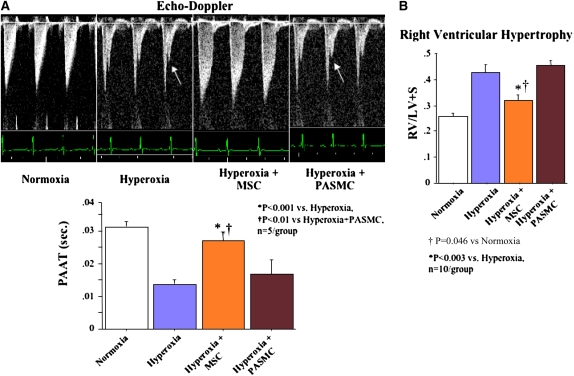
Figure 6.
Intratracheal bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC) administration prevents pulmonary hypertension associated with O2-induced lung injury. (A) Pulmonary arterial acceleration time (PAAT). PAAT was significantly decreased in chronic hyperoxia–induced lung injury and showed a characteristic notch indicating pulmonary hypertension (arrows). Intratracheal BMSCs, but not pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs), restored the PAAT almost to control levels. (B) Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH). Hyperoxic-exposed rats had significant RVH as indicated by the increase in RV/LV+S (right ventricle/left ventricle plus septum) ratio compared with normoxic controls. Intratracheal BMSCs, but not PASMCs, reduced RVH.