FIG. 13.
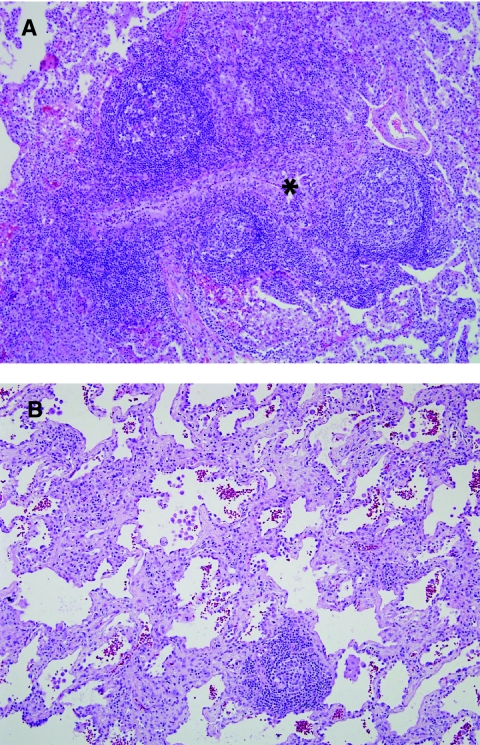
Autoimmune and rheumatologic disease. Histologic patterns associated with autoimmune disease include prominent lymphoid hyperplasia, nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) pattern, lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia pattern, interstitial fibrosis, pulmonary arterial disease, and pleural disease. Increased numbers of interstitial plasma cells may be a clue to autoimmune etiology. (A) Follicular bronchiolitis is one form of lymphoid hyperplasia in the lung (compressed bronchiole, *). (B) This patient with juvenile idiopathic arthritis showed a pattern of cellular and fibrosing NSIP on lung biopsy.