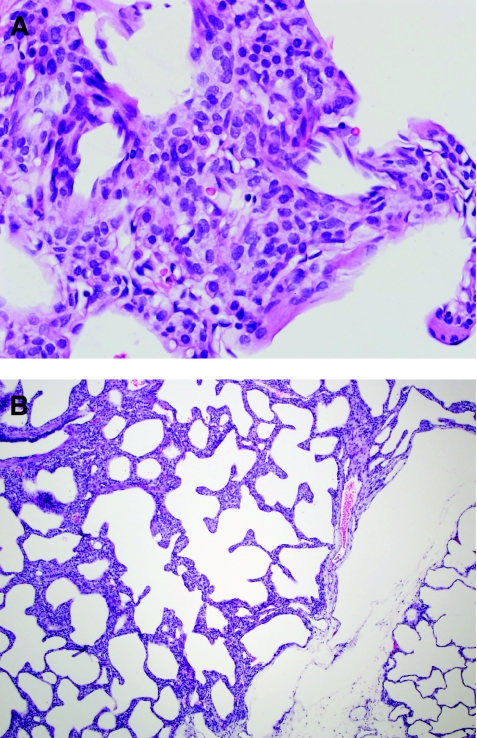
FIG. 6.
Pulmonary interstitial glycogenosis. (A) Pulmonary interstitial glycogenosis (PIG), also called infantile cellular interstitial pneumonia (ICIP), is characterized by increased numbers of bland ovoid mesenchymal cells within the interstitium of the lung. It is thought to be a secondary reaction to a variety of forms of lung injury in neonates and young infants. (B) This process is often patchy in distribution and is commonly associated with disorders of alveolar growth.