Figure 1.
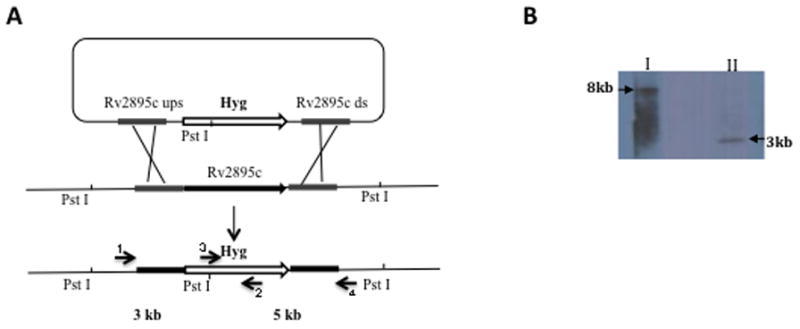
Strategy for generation of a knock out mutant of Rv2895c in H37Rv. The Rv2895c gene was replaced with a hygromycin (Hyg) resistance cassette by phage transduction and homologous recombination. A) Scheme of the genome region containing Rv2895c and the substrate used for homologous recombination. Position of the PstI restriction sites used for chromosomal DNA digestion and the primers used for PCR amplification. B) Southern blot to confirm the ST212 mutant. The genomic DNA of H37Rv and ST212 was completely digested with PstI enzyme and the blot was probed with a fragment containing the 500 bp upstream Rv2895c. The PstI restriction sites in the vicinity of Rv2895c in wild type H37Rv are 8 kb apart (I) whereas restriction of ST212 DNA generates a 3 kb band (II), since the Hyg cassette has an internal PstI site. Gene replacement was also confirmed by PCR and sequencing. Primers 1 and 4 were designed in the region upstream and downstream of Rv2895c. Primers 2 and 3 are internal primers of the Hyg cassette. PCR was done using primers 1 and 2 and primers 3 and 4 with DNA from both wild type and mutant. No product was obtained using the wild type DNA whereas products of 2kb and 1.4kb were obtained using DNA isolated from the mutant as template. Sequencing of the PCR products confirmed the homologous recombination and gene replacement.
