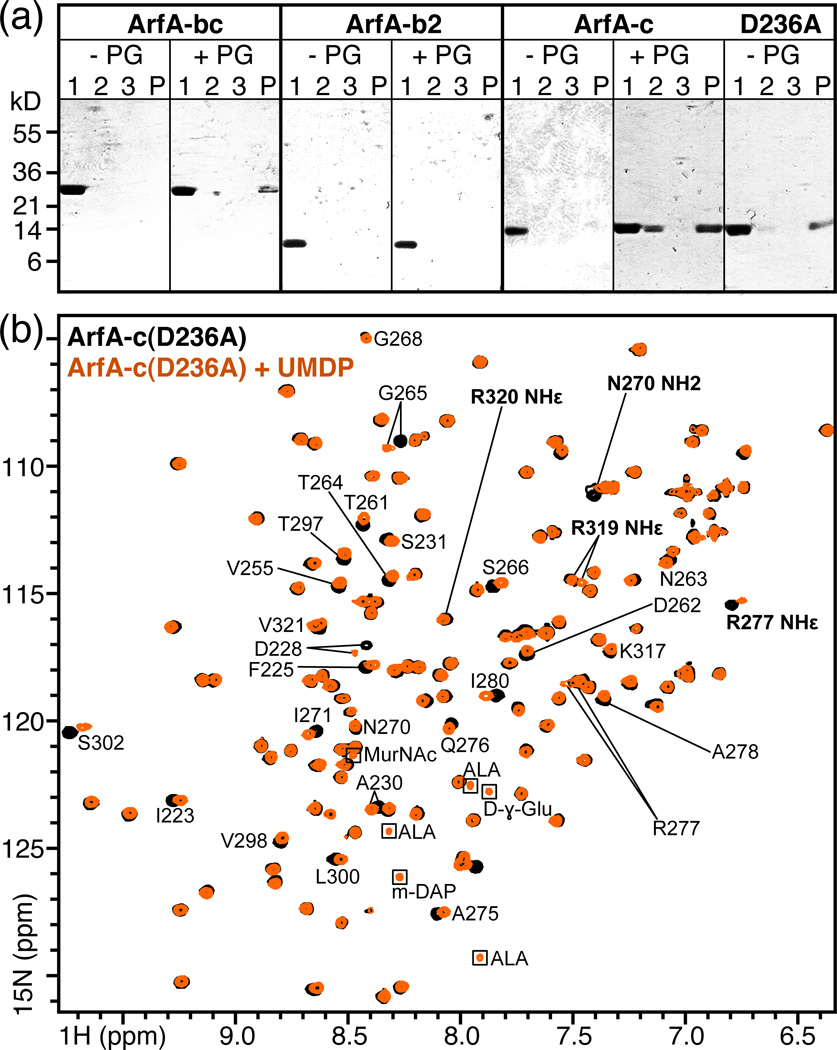
Figure 4. Association of ArfA-c with peptidoglycan.
(a) Soluble, purified ArfA polypeptides: ArfA-bc, ArfA-b2 (residues 73–197), ArfA-c and ArfA-c(D236A) were mixed with purified peptidoglycan from M. tuberculosis (+PG). As negative controls, proteins were incubated without peptidoglycan (−PG). After 2 hr incubation, the supernatant (Lane 1) and insoluble fraction were separated by centrifugation, the pellet was washed with buffer and again separated from the supernatant (Lane 2) by centrifugation. After a second wash and centrifugation step to generate a third supernatant (Lane 3) and final pellet (Lane P), all fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and visualized with Coomassie blue. ArfA-bc, ArfA-c and ArfA-c(D236A) bind peptidoglycan and separate with it in the insoluble fraction, while ArfA-b2 does not bind peptidoglycan and remains in solution. For each ArfA polypeptide, the result of one out of two or more independent experiments is shown. (b) NMR 1H/15N HSQC spectra of ArfA-c(D236A) obtained at pH7, 25°C, with (orange) or without (black) ~20 molar equivalents of UMDP. Examples of peaks sensitive (e.g. D228) or insensitive (e.g. G268) to addition of UMDP are labeled. Peaks from side chains are labeled in bold. Peaks from the natural abundance peptide are enclosed in boxes.