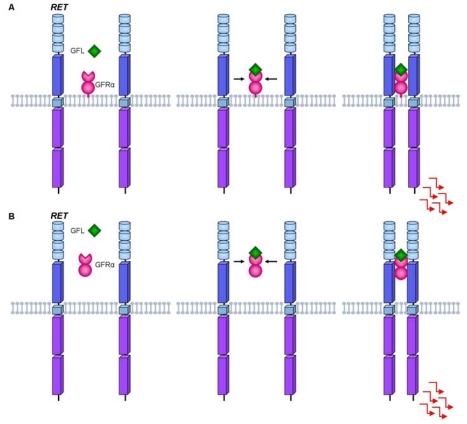
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of ligand-mediated RET activation. (A) In the cis model RET activation: the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) family of ligands (GFL) binds to membrane glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored GDNF-family coreceptors (GFRα). The activation leads to dimerization of RET and consequently activation of the intracellular signaling pathways; (B) In the trans model RET activation: the ligand binds to the soluble form of its coreceptor (GFRα) and the ligand-GFRα complex brings together two inactive RET monomers. Ligand-induced activation induces dimerization and tyrosine phosphorylation of the RET receptor with downstream activation of several signal transduction pathways.