Fig. 1. Pathway of prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis.
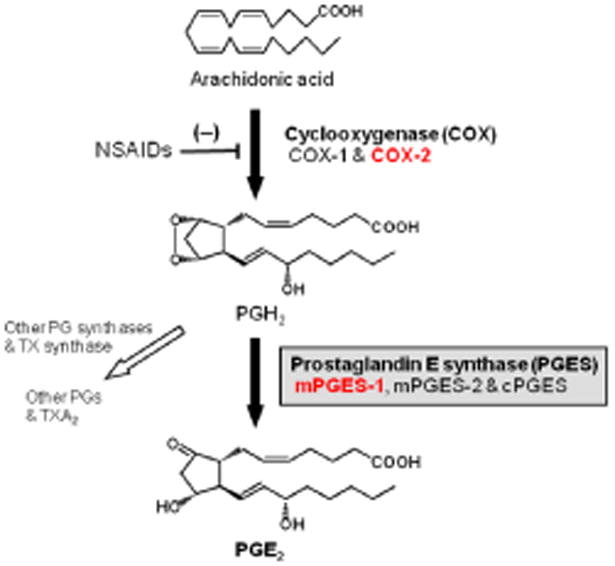
Arachidonic acid is converted to the unstable metabolite, prostaglandin (PG) H2 by two isozymes of cyclooxygenase (COX), constitutive COX-1 and inducible COX-2. PGH2 is then converted to PGE2 by prostaglandin E synthase (PGES). There are at least 3 isozymes of PGES, including microsomal PGES (mPGES) -1, mPGES-2 and cytosolic PGES (cPGES). PGH2 is also metabolized to other PGs by each specific PG terminal synthases (PGDS for PGD2, PGFS for PGF2α and PGIS for PGI2) and to thromboxane (TX) A2 by TXS. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) inhibit PGs and TXA2 production by inhibiting COXs.
