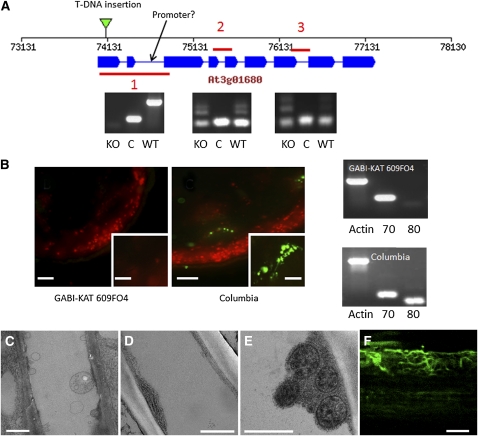
Figure 5.
SEOR1 Mutant-DNA Insertion Line.
(A) A representation of the Arabidopsis gene At3g01680 indicating the location of the T-DNA insertion in the GABI-KAT 609F04 line and the location of a possible weak promoter indicated by analysis using PlantpromoterDB 2.0 (http://ppdb.agr.gifu-u.ac.jp/ppdb/cgi-bin/index.cgi). Also shown are three sections amplified by RT-PCR showing that a truncated mRNA product containing sections 2 and 3 is produced in the T-DNA insertion mutant. C, amplification control; KO, GABI-KAT 609f04; WT, wild-type Arabidopsis line Columbia.
(B) Immunolocalization using a P protein–specific antibody indicates P proteins are absent in GABI-KAT 609F04 (insets are higher magnification images of single vascular bundles), and RT-PCR analysis shows the expression of the adjacent gene At3g01670 (70) is unaffected in the At3G01680 (80) T-DNA insertion mutant (Actin serves as an amplification control).
(C) TEM micrograph of SEOR1 T-DNA insertion mutant after standard chemical fixation. Filaments filling the lumen of the sieve tube as shown in Figure 3 are absent.
(D) and (E) TEM micrographs of At SEOR1 T-DNA insertion mutant after freeze substitution of whole plants. At SEOR1 filaments are absent, but all other structures, such as ER, mitochondria, and clamps proteins surrounding the mitochondria, are present.
(F) Transformation of KO:GABI-KAT 609f04 with At SEOR1-GFP leads to filament formation.
Bars = 100 μm in (B) (inset = 20 μm), 1 μm in (C), 500 nm in (D) and (E), and 3 μm in (F).