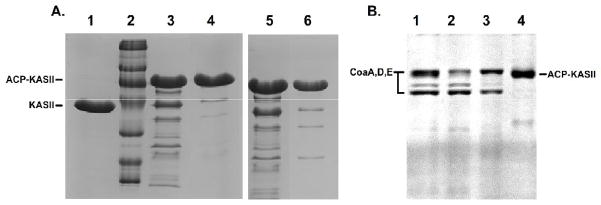
Figure 2.
(a) Size exclusion (left) and ion-exchange chromatography (right) were used to purify the ACP-KS complex from the other enzymes in the reaction. The unreacted KS domain is shown in lane 1 and a size standard is in lane 2. The crude reaction mixture, with all His6-tagged enzymes is shown in lanes 3 and 5. The fractions containing the ACP-KS fusion purified by traditional chromatography are shown in lanes 4 and 6. The purified fractions still show residual amounts of enzymes from the reaction. (b) The purification of ACP-KS from the reaction using orthogonal enzymes. The crude reaction mixture is seen in lane 1, where CoaA, CoaD, and CoaE appear as bands. Native Sfp is sufficiently dilute to not appear as a band. Nickel resin flowthrough is shown in lane 2. 50mM and 200mM elutions of the nickel resin are shown in lanes 3 and 4. In lane 4, only ACP-KS elutes from the resin.