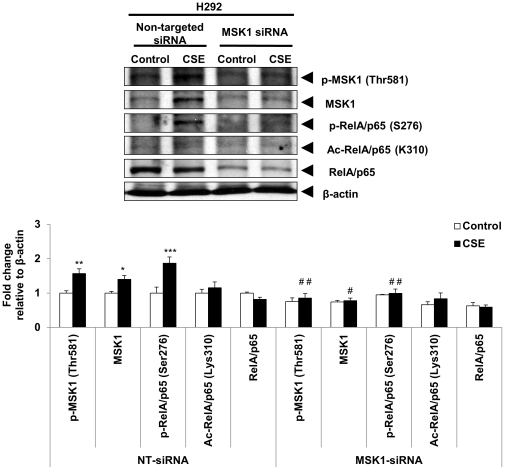
Figure 5. siRNA-mediated knock-down of MSK1 in H292 cells attenuated the phosphorylation of RelA/p65 by CSE treatment.
MSK1 knock-down by siRNA approach attenuated the phosphorylation of RelA/p65 by CSE in human bronchial epithelial cells. H292 cells were transfected with 100 nM scrambled siRNA (non-targeted siRNA) or siRNA directed against MSK1 (MSK1 siRNA) for 24 h, followed by starvation in serum free medium and treated for 1 h after 72 h of transfection with CSE (1%). Whole cell lysate was prepared after 1 h treatment and assayed for effect of MSK1 knock-down by immunoblotting. The levels of p-MSK1 (Thr581), total MSK1, phosphorylated RelA/p65 (Ser276), acetylated RelA/p65 (Lys310), and total RelA/p65 were determined by immunoblotting. β-actin was used as a loading control. Gel pictures are representative of at least three separate experiments. The band intensity was measured by densitometry and data shown as fold change relative to β-actin control. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001, significant compared with control or without treatment non-targeted siRNA group; #, P<0.05; ##, P<0.01, significant compared to CSE treated non-targeted siRNA group.