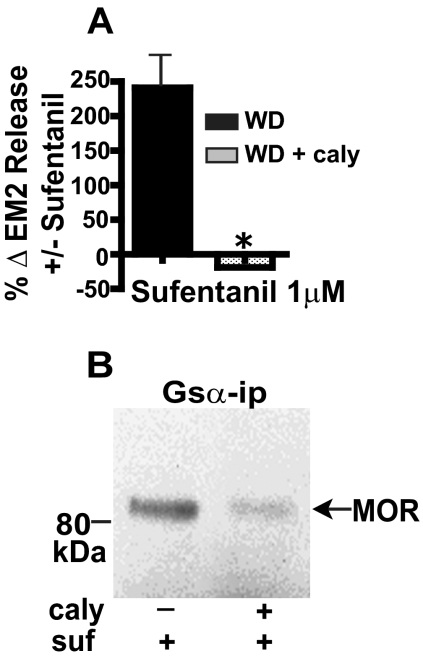
Fig. 2.
Inhibition of PP2A activity blocks both the stimulation of evoked EM2 release by sufentanil and its enhancement of MOR Gsα coupling in opioid-withdrawn spinal tissue of male rats. A, intrathecal pretreatment with the PP2A inhibitor calyculin A (caly) abolished the sufentanil (1 μM) stimulation of evoked EM2 release from opioid-withdrawn spinal tissue of males (WD + caly; n = 3; p < 0.01). Sufentanil (1 μM) stimulation of evoked EM2 release (WD) is replicated from Fig. 1B to facilitate comparison. B, CoIP of MOR with Gsα was determined in parallel from withdrawn spinal tissue in the absence of intrathecal treatment (left) and after intrathecal treatment (right) with calyculin A (n = 3). Inhibition of spinal PP2A abrogated both the withdrawal-associated augmented facilitatory modulation of EM2 release by sufentanil as well as the enhanced coupling of MOR to Gs.