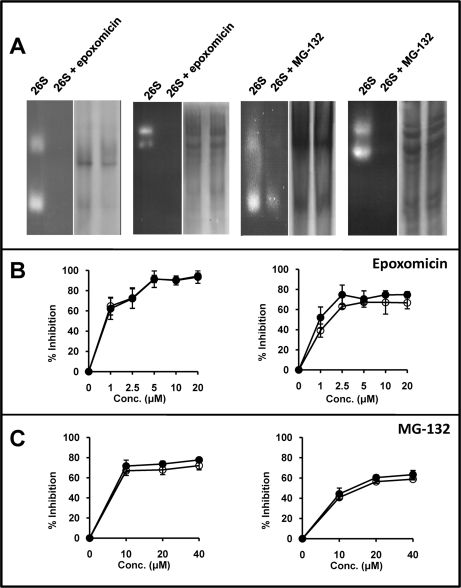
Fig. 7.
Activity of the 26S proteasome in the presence or absence of proteasome-inhibitors. A, In-gel hydrolysis of site-specific fluorogenic substrates by partially purified 26S proteasomes, which include significant amounts of 20S proteasomes, incubated or not with 2.5 μm epoxomicin or 20 μm MG-132. The experiments were performed in 3% polyacrylamide gel or 3–15% polyacrylamide gradient gels for the tryptic (Boc-LRR-amc) and chymotryptic (Suc-LLVY-amc) substrates, respectively. For each experiment the in-gel digestion analysis is shown on the left side. The same gel, washed and stained with Coomassie blue, is shown at right. B, Inhibition of the hydrolysis of fluorogenic substrates specific for the chymotryptic (left) or tryptic (right) activity by partially purified 26S proteasomes in the presence of various concentrations of epoxomicin. Empty circles (o) show the results obtained with proteasome purified from cells treated with the inhibitor. Black circles (●) show results obtained with proteasome treated with the inhibitor after its purification from cells. C, Inhibition of the hydrolysis of fluorogenic substrates specific for the chymotryptic (left) or tryptic (right) activity by partially purified 26S proteasomes in the presence of various concentrations of MG-132. Conventions are as in panel B.