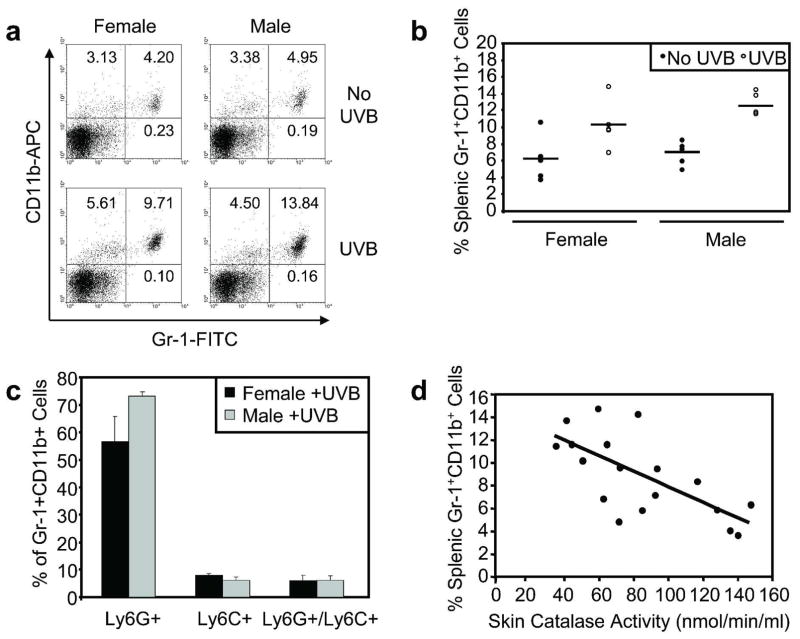
Figure 2. Acute UVB exposure increases the percentage of Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells in the spleen.
Male and female mice were exposed to a single UVB dose (n=5 per sex). a, Splenic myeloid cells were assessed by flow cytometric analysis of Gr-1 and CD11b surface staining at 48 hours following UVB exposure and in non-irradiated mice. b, Relatively low percentages of splenic Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells were detected in non-irradiated male and female control mice. UVB significantly increased splenic Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cell percentages in male (p=0.0022) and female (p=0.0057) mice. Horizontal bars represent means. c, Ly-6G and Ly-6C were analyzed separately to characterize Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cell subsets. The majority of UVB-induced splenic Gr-1+CD11b+ cells were Ly-6G-positive/Ly-6C-negative. d, Skin catalase activity and splenic Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cell percentage were compared in all mice. A significant inverse correlation was detected (r = −0.69; p=0.0015).