Figure 1. Annotated mouse SGK1 (A), GILZ1 (B) and CNK3 (C) protein schematics showing key motifs and interaction domains.
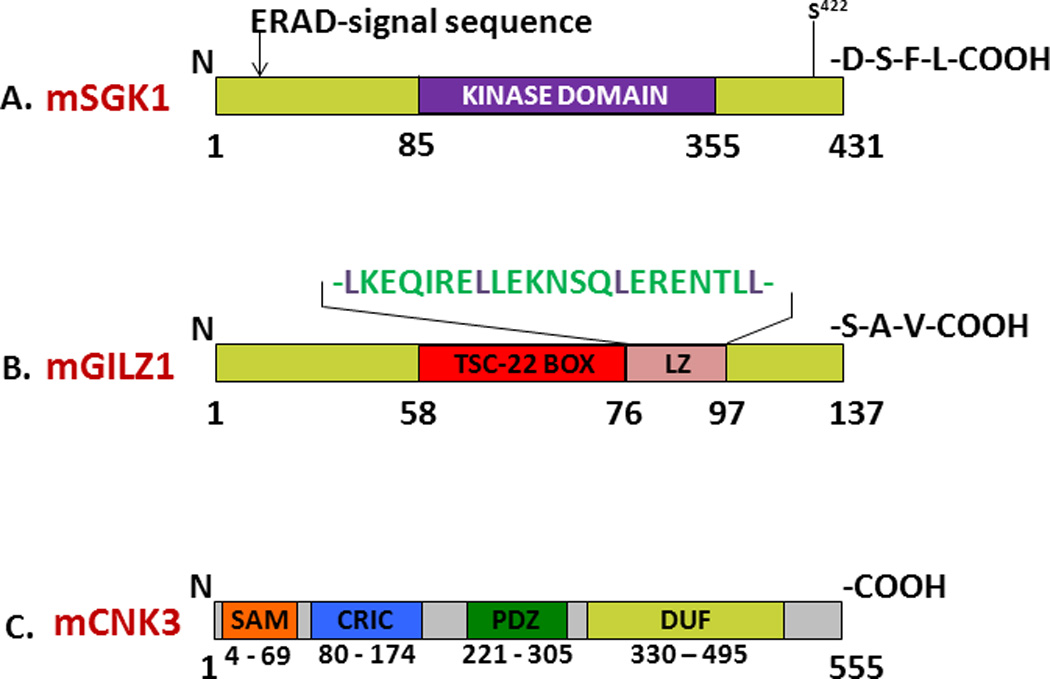
A. SGK1 is an important aldosterone-regulated protein kinase that stimulates renal ENaC function. The ER-associated degradation signal (or ‘degron’) lies within the N-terminus of SGK1, upstream of its kinase domain. The Ser residue within the hydrophobic motif that is critical for mTORC2-dependent kinase activation is depicted. SGK1 also possesses a standard Class I PDZ domain-interaction motif at its C-terminus. B. GILZ1 is a small aldosterone-induced chaperone that plays a central role in protein trafficking and signaling. The TSC-22 signature box defines region of homology with the TGFβ-stimulated clone-22 protein and other family members. The leucine zipper (LZ) motif mediates GILZ dimerization. Also shown is the sequence of the Class I PDZ domain-interaction motif at the C-terminus. C. CNK3 is a recently identified MR-target shown to be critical for ENaC activity. As with other members of the CNK family, CNK3 contains a sterile-α-motif (SAM), a conserved-region-in-CNK (CRIC) domain, a classic PDZ domain, and a downstream region commonly referred to as the domain-of-unknown-function or DUF.
