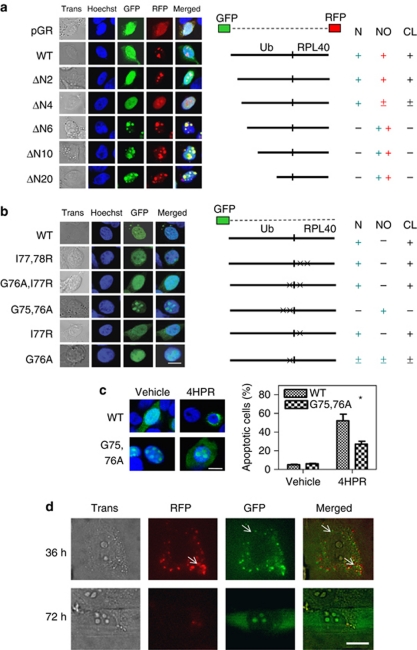
Figure 5.
Cleavage of the Ub hybrid proteins. (a) The Hep3B cells grown on coverslips were transiently transfected with 2 μg of the plasmid encoding the wild-type Uba52 or the deletion mutant Uba52 that was end-tagged with both GFP (N-terminal) and RFP (C-terminal), or with a vector control (pGR). GFP and RFP fluorescence was analyzed using a Zeiss LSM 510 confocal microscope. ΔN2, ΔN4, ΔN6, ΔN10 and ΔN20 indicate the deletion mutants of Uba52 lacking the N-terminal 2, 4, 6, 10 and 20 amino acids, respectively. Nuclear (N) or nucleolus (NO) indicates localization of Ub or RPL40, respectively, which was derived from the Ub hybrid protein Uba52 by cleavage (CL) Trans, transmission. (b) The Hep3B cells grown on coverslips were transiently transfected with 2 μg of plasmid encoding the wild-type or mutant GFP-Uba52 or with a vector control (GFP). I77,78 R indicates a mutant in which I77 and I78 are mutated to R. In G76A/I77R, G76 and I77 are mutated to A and R, respectively. In G75,76A, G75 and G76 are mutated to A. In I77R, I77 is mutated to R. In G76A, G76 is mutated to A (scale bar, 10 μm). (c) Effect of the G75,76A (cleavage-resistant) mutation on drug-induced apoptosis in Hep3B cells. Cells grown on coverslips were transiently transfected with 2 μg of the plasmid encoding the wild-type or mutant GFP-Uba52 (G75,76A) and treated with 10 μM 4HPR for 3 days. The cells with apoptotic morphology were identified by confocal microscopy (left panels), and the apoptotic cells among the GFP-positive cells were quantified (right panels). Each bar represents the mean of triplicate experiments±S.E.M. (*P< 0.05); scale bar, 10 μm. (d) Visualization of wild-type Uba80 in living Hep3B cells using a TIRF microscope with a transmitted all-side polished dove prism. Hep3B cells grown on coverslips were transiently transfected with 10 ng of the plasmid encoding wild-type Uba80 tagged with both RFP (N-terminal) and GFP (C-terminal). The TIRF image was examined 36 and 72 h after transfection; bar, 10 μm