Figure 3.
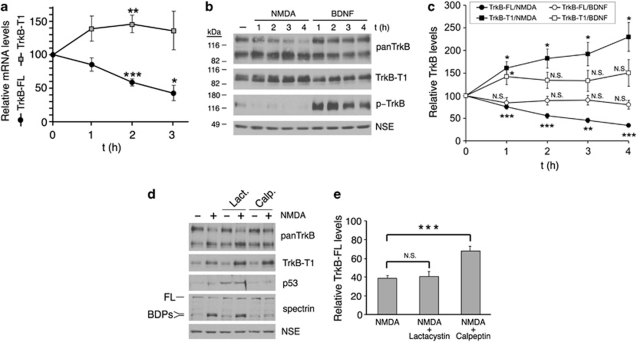
Two different mechanisms contribute to TrkB regulation in excitotoxicity. (a) Quantitative RT-PCR of TrkB-FL and TrkB-T1 mRNAs. Relative mRNA levels (mean±S.E.M., n=3 experiments) were established after normalization to 18S rRNA and comparison with untreated cells, which were arbitrarily assigned a value of 100%. The effect of NMDA was assessed using a Student's unpaired t-test (*P<0.05, **P <0.01, and ***P<0.001). Reverse regulation of isoform mRNAs producing a progressive increase in the fraction of TrkB-T1 mRNA was observed. (b) Contrary to NMDA stimulation, treatment with BDNF (100 ng/ml) for 1−4 h induced TrkB activation, established by phospho (p)-TrkB detection with p-TrkA (Tyr490)-specific antibodies, but no general modification of TrkB-FL, tTrkB, or TrkB-T1. (c) Quantitation of TrkB-FL and TrkB-T1 levels in cultures treated with NMDA and BDNF showed that BDNF-induced mechanisms were not contributing to TrkB regulation induced by excitotoxicity. Levels of TrkB-FL and TrkB-T1 (mean±S.E.M., n=10 experiments) were compared with the levels in untreated neurons, which were arbitrarily assigned a value of 100%. Student's unpaired t-test was used to evaluate the differences between treated or untreated cultures (N.S., nonsignificant; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001). (d) TrkB-FL is processed by a calpain-dependent mechanism during excitotoxicity. Cultures were preincubated with protease inhibitors lactacystin (20 μM) or calpeptin (10 μM) before NMDA treatment for 2 h. The processing of FL brain spectrin to produce characteristic breakdown products (BDPs) was used as a standard assay of calpain activity, whereas levels of p53 were analyzed to confirm proteasome inhibition. (e) Quantitation of TrkB-FL revealed calpain-dependent processing as the major mechanism of NMDA-induced TrkB regulation. Cultures were preincubated and treated with lactacystin or calpeptin as described above. Normalized TrkB-FL levels (mean±S.E.M., n=8 experiments) in neurons treated with NMDA, with or without protease inhibitors, were compared with the corresponding levels found in control neurons without NMDA, which were arbitrarily assigned a value of 100%. Student's unpaired t-test was used to evaluate the differences in the NMDA-treated cultures between those with or without calpain inhibitor preincubation (N.S., nonsignificant; ***P<0.001)