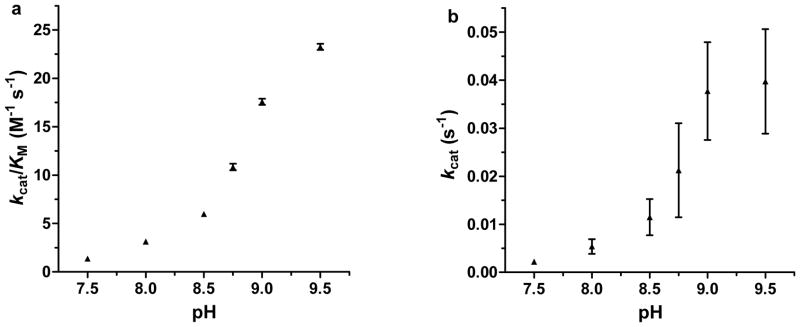
Figure 3. pH-dependency of pNPA hydrolysis by [Hg(II)]S[Zn(II)(H2O/OH−)]N(TRIL9CL23H)3n+.
Plots of a, kcat/KM vs. pH and b, kcat vs. pH for the hydrolysis of pNPA by [Hg(II)]S[Zn(II)(H2O/OH−)]N(TRIL9CL23H)3n+ (10 μM). pKa values of 8.82 ± 0.11 and 8.77 ± 0.08 for plots a and b, respectively, can be determined from the fittings and presumably represent the deprotonation of Zn-OH2 to form an active Zn-OH− nucleophile, as with CAII. See Supplementary Methods for a description of the fitting and error analysis.