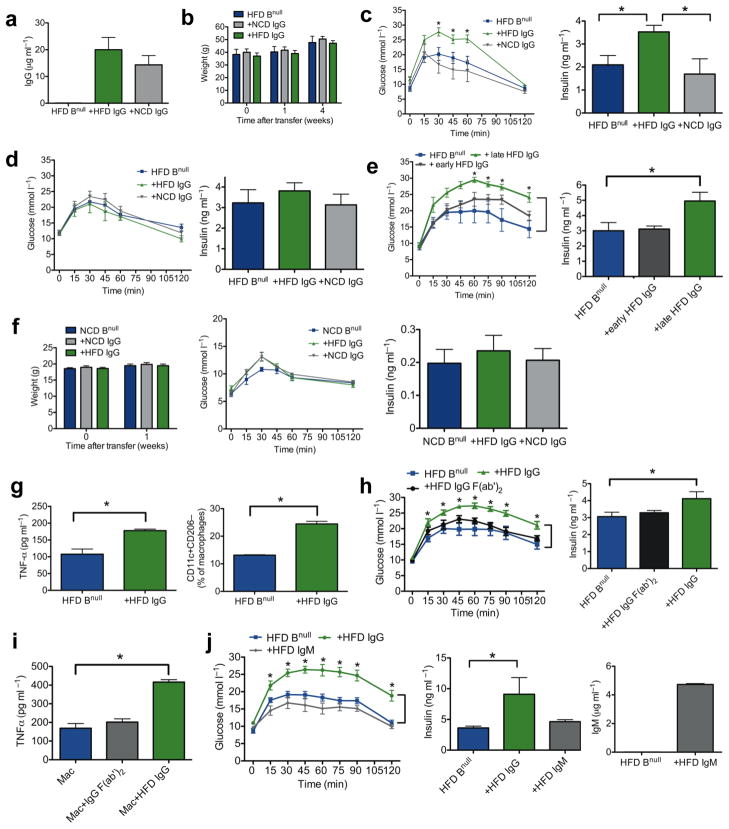
Figure 4. IgG antibodies from obese mice induce abnormal glucose metabolism in recipient Bnull mice.
(a) Serum concentration of IgG in Bnull mice one week following i.p. IgG injection (n = 3). (b) Body weights of HFD Bnull recipient mice after IgG transfer (representative of 3 experiments, n = 4). (c) GTT (left, * P < 0.05) and fasting insulin (right, *P < 0.05) one week following transfer of IgG into 16 week old HFD Bnull mice (representative of 3 experiments, n = 4). (d) GTT (left) and fasting insulin (right) four weeks following transfer of IgG (representative of 2 experiments, n = 4). (e) GTT (left, *P < 0.05) and fasting insulin (right, *P = 0.048) one week following transfer of late or early IgG (n = 5). (f) Weights (left), GTT (center), and fasting insulin (right) of 6 week old NCD Bnull mice 1 week after IgG transfer (representative of 2 experiments, n = 4). (g) TNF-α from VAT SVC cultures (left, *P = 0.04, 2 experiments, 6 mice) and M1 macrophages in HFD Bnull VAT one week after IgG transfer (right, *P = 0.007, 2 experiments, 6 mice). (h) GTT (left, *P < 0.05) and fasting insulin (right, *P = 0.04) one week after transfer of HFD Ig (n =5). (i) TNF-α from HFD Bnull VAT macrophages stimulated in vitro with HFD IgG (*P= 0.007), or HFD F(ab′)2 (n = 3). j) GTT (left) and fasting insulin (middle) of HFD Bnull mice 1 week after receiving HFD Ig (n = 5, *P < 0.05). Serum concentration (right) of IgM in HFD Bnull mice 1 week following IgM injection (n = 3). Graphs are means ± s.e.m.